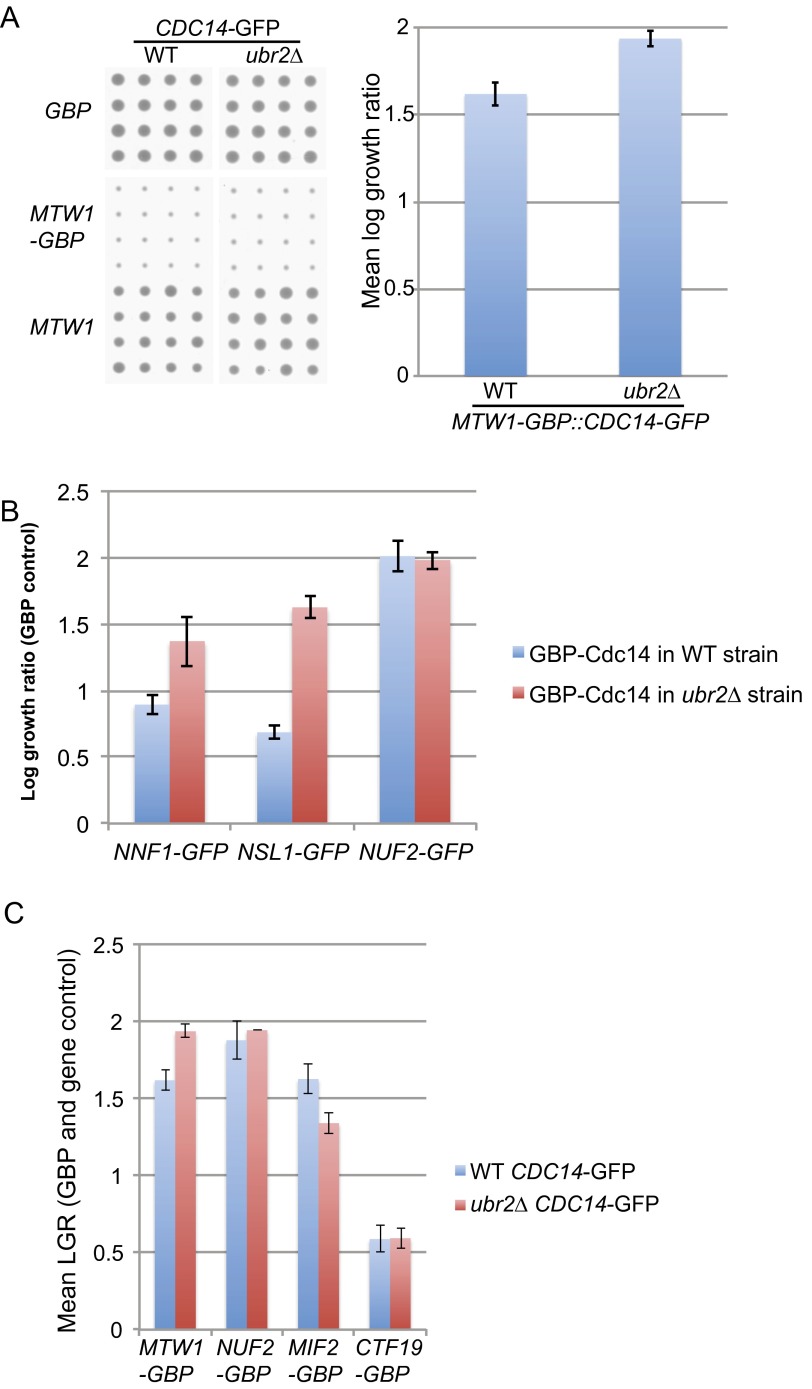
Fig. S8.
Deleting UBR2 does not rescue the growth defect of MTW1-GBP: CDC14-GFP SPI. (A) The three plasmid constructs (MTW1-GBP, MTW1, and GBP) were introduced into strains containing CDC14-GFP as before but now in both wild-type and ubr2∆ backgrounds and arrayed with 16 replicates. The average of the MTW1 and GBP controls versus the MTW1-GBP experiment (mean LGR) were compared and show that the ubr2∆ strain is also inhibited by Cdc14 fusion to Mtw1 (error bars = SD of the two controls). (B) Deletion of UBR2 does not rescue several Cdc14 SPIs, including Nnf1, Nsl1, and Nuf2; if anything, the SPIs are stronger in a ubr2∆ strain. Errors bars are SD of the mean. (C) We also created additional GBP constructs, including NUF2-GBP and CTF19-GBP (both of which were Cdc14 SPIs) (Fig. 5) and MIF2-GBP, which gave a weak Cdc14 SPI with both controls (Dataset S5). None of these are suppressed by the ubr2∆ mutation (Mtw1 data as in A; error bars = SD of the two controls).