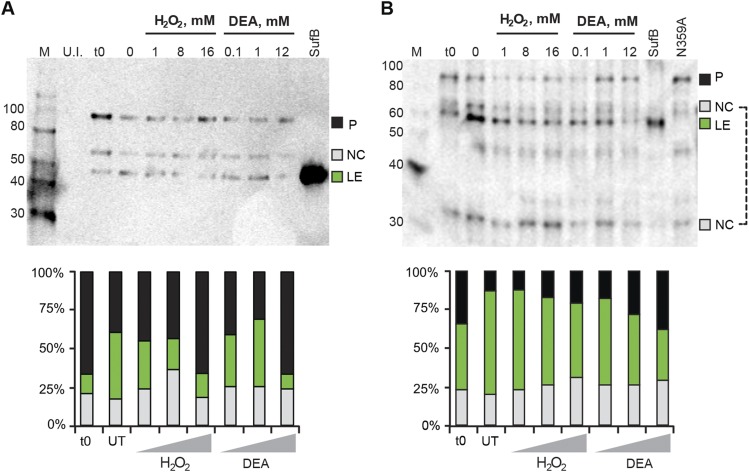
Fig. S3.
SufB intein with native exteins undergoes N-terminal cleavage. (A) C-extein antibody blot. Full-length, His-tagged SufB was overexpressed and treated with H2O2 and DEA, similar to Fig. 3 C and D. The lysates were separated by 12% SDS/PAGE and transferred to Immuno-Blot PVDF (Bio-Rad). An anti–C-extein antibody was used to probe splicing products at 1:5,000 dilution. The blot shows N-terminal cleavage, which increases with 1 mM and 8 mM H2O2 and all concentrations of DEA treatment. Again, similar to Fig. 3 C and D, the highest concentrations of H2O2 and DEA cause precursor accumulation. The SufB lane is purified inteinless M. smegmatis SufB protein as size control for ligated exteins. Products detected are: precursor (P; 96 kDa), N-terminal cleavage product (NC, intein+C-extein; 66 kDa) and ligated exteins (LE; 56 kDa). (B) SufB (ligated extein) antibody blot. The same lysates from panel A were separated and probed using a SufB antibody at 1:5,000 dilution. N-terminal cleavage is seen at all concentrations of H2O2 and DEA, and as in A, precursor accumulation occurs at the highest concentrations for both treatments. The 66-kDa NC band was used for N-terminal cleavage quantitation. An additional N-terminal cleavage product, the N-extein (NC; 30 kDa), is seen with this antibody. Western blots were scanned on a Typhoon imager and quantified using ImageQuant. Polyclonal antibodies were produced in rabbits against purified SufB protein of M. smegmatis or a synthetic C-extein peptide CVEPIAKELPMEYALE by Covance. Because of differential reactivity with polyclonal antibodies, ratios of different species in the Western blots are arbitrary, unlike fluorescence quantitation.