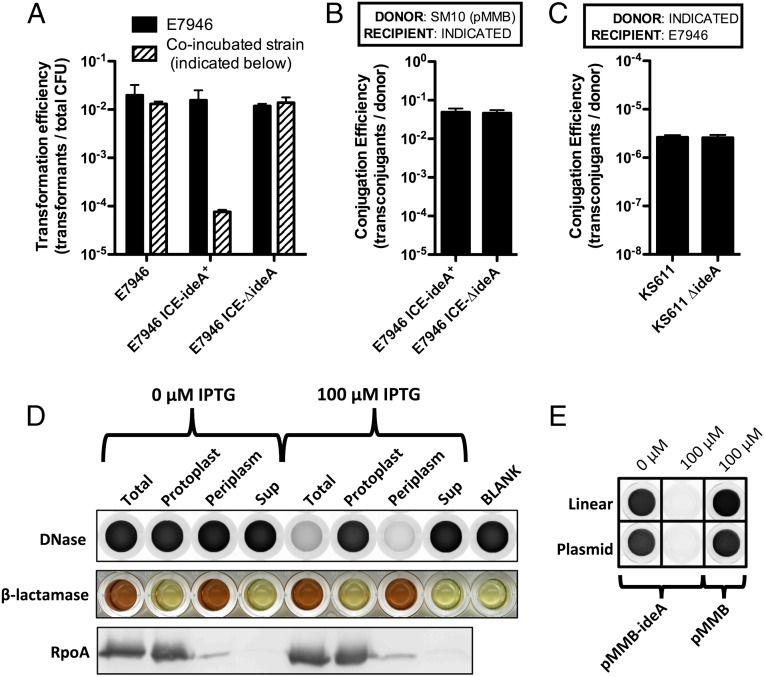
Fig. 2.
IdeA is a periplasmically localized DNA endonuclease that acts in cis to inhibit natural transformation of V. cholerae. (A) Natural transformation assays where E7946 was coincubated with the indicated strain on chitin. Cells were transformed with 0.5 μg of a PCR product that confers resistance to kanamycin. Transformation efficiency of E7946 is shown in black bars and that of the coincubating strain in stippled bars. (B) Conjugation of pMMB from an E. coli SM10 donor into the indicated V. cholerae strains. (C) Conjugation of the ICE from the indicated donor V. cholerae strain into a naive E7946 recipient. (D) Enzyme activity assays and Western blot analysis of cellular fractions of E7946 containing pMMB-ideA grown in the presence of the indicated concentration of IPTG. DNase activity, indicated by a loss of fluorescent signal in this assay (i.e., clearing from black to white) was measured in each fraction using 2 μg of linear DNA as a substrate for cleavage. β-lactamase activity, a periplasmic marker, was measured in cellular fractions using nitrocefin, a colorimetric substrate that changes color from yellow to red in the presence of β-lactamase activity. RpoA, a cytoplasmic marker, was also assessed by Western blot analysis in each cellular fraction. (E) DNase activity assay of periplasmic fractions of E7946 containing the indicated plasmid grown in the presence of the indicated concentration of IPTG using linear DNA (salmon sperm DNA) or supercoiled plasmid DNA (pGhost9) as a substrate for measuring DNase activity. Data in A–C are shown as the mean ± SD and the result of at least two independent experiments. Data in D and E are representative of at least two independent experiments.