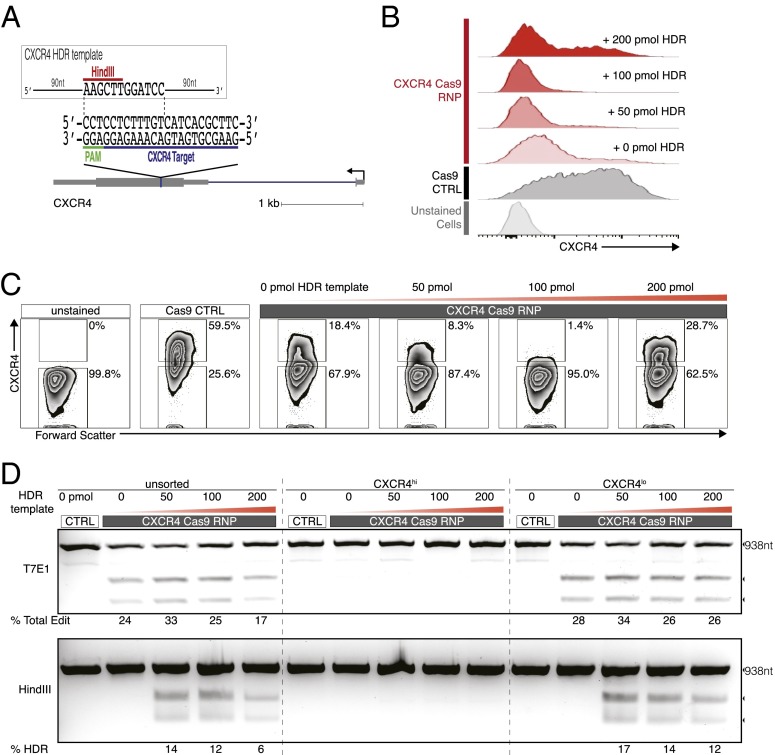
Fig. 2.
Efficient homology-directed repair allows targeted DNA replacement in primary human T cells. (A) Schematic representation of single-stranded oligonucleotide HDR template with 90-nt homology arms designed to replace 12 nt, including the PAM sequence, and introduce a novel HindIII restriction enzyme cleavage site (red) at the CXCR4 locus, where the Cas9 RNP cleaves. sgRNA target (blue) and PAM (green) sequence are indicated. (B) Histograms of CXCR4 cell-surface staining assessed by flow cytometry in CXCR4 Cas9 RNP-treated cells in the presence of varying concentrations of single-stranded HDR template (compared with control Cas9 protein-treated cells and unstained cells). (C) FACS plots (corresponding to histograms in B) show maximal ablation of CXCR4 with Cas9 RNP treatment and 100 pmol of HDR template. (D) T7E1 assay was used to estimate the “% Total Edit” (defined as the sum of all NHEJ and HDR events that gives rise to indels at the Cas9 cleavage site), whereas HDR frequency was determined by HindIII digestion, which specifically cleaved the newly integrated HindIII site, and was calculated as the ratio of DNA product to DNA substrate. Expected PCR product size (938 nt) and approximate expected T7E1 and HindIII digestion fragments are indicated.