Fig. 3.
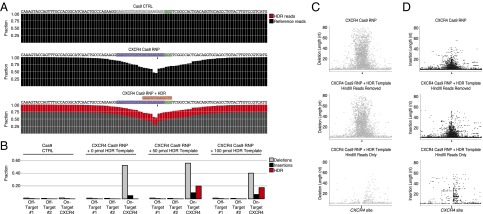
Quantitative analysis of Cas9 RNP-mediated editing and HDR by deep sequencing. (A) CXCR4 Cas9 RNP-mediated indels and HDR from experiments in Fig. 2 were analyzed by targeted deep sequencing of the CXCR4 locus. A total of 100 nt centered on the predicted cut site are shown with sgRNA target (blue), PAM (green), and predicted sequence after HDR genome targeting (red). At each position, the fraction of reads that correctly aligned to the reference genome (black) or HDR template-derived sequence (red) are shown. Although rare (∼1–2%), edits were detected with Cas9-only control treatment, including at the predicted CXCR4 cut site, potentially indicating trace amounts of experimental contamination of the Cas9 RNPs. (B) Bar graph summarizes the fractions of reads edited with deletions (gray), insertions (black), or successful HDR targeting (red) in Cas9 CTRL, CXCR4 Cas9 RNP, and CXCR4 Cas9 RNP cells with 50 or 100 pmol CXCR4 HDR template at the CXCR4 site and two predicted off-target sites. Reads with HDR template-derived sequence incorporated were removed to calculate fractions with deletions and insertions (Dataset S1). Scatter plots show the genomic localization (±100 nt around the expected Cas9 cut side; chromosome 2: 136873140–136873340) and the length of (C) deletions and (D) insertions. (Top) Deletions/insertions for CXCR4 RNP-treated cells. (Middle) Deletions/insertions in reads without HDR template sequence incorporated in cells treated with CXCR4 RNP and CXCR4 HDR template. (Bottom) Deletions/insertions in reads with HDR template-derived sequence incorporated. Arrowheads indicate approximate location of expected Cas9 cut site.
