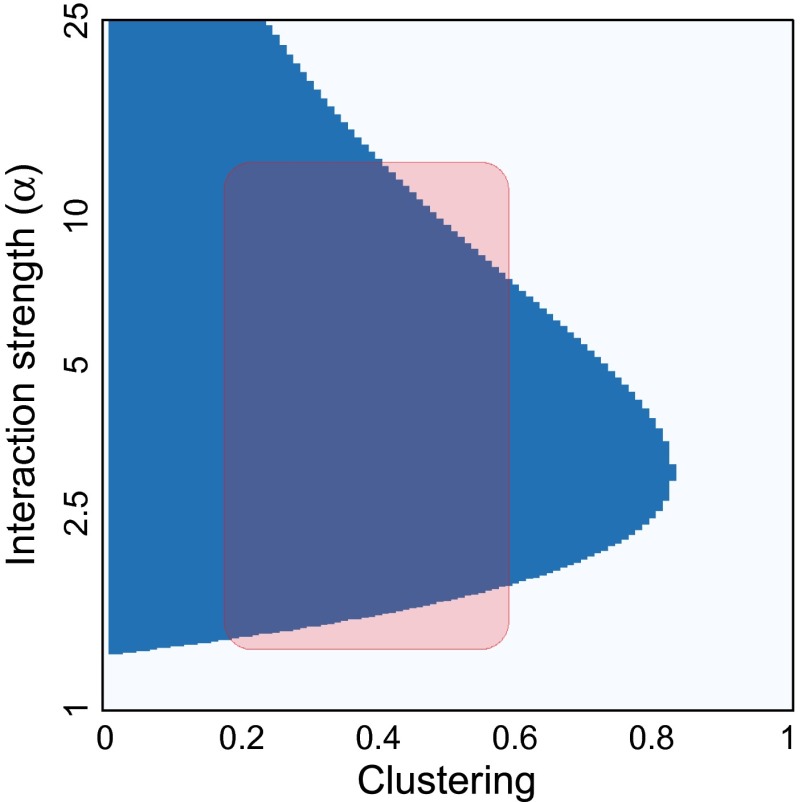
Fig. 3.
Effects of clustering hold over a broad range of parameters. The clustering criterion is used to investigate which network—a clustered structure (blue) or its equivalent random network (white)—propagates faster in varying interaction strength and clustering. The other parameters are set to those of Fig. 2. The shaded region is used to indicate a range of possible realistic scenarios for influenza and PC pneumonia.