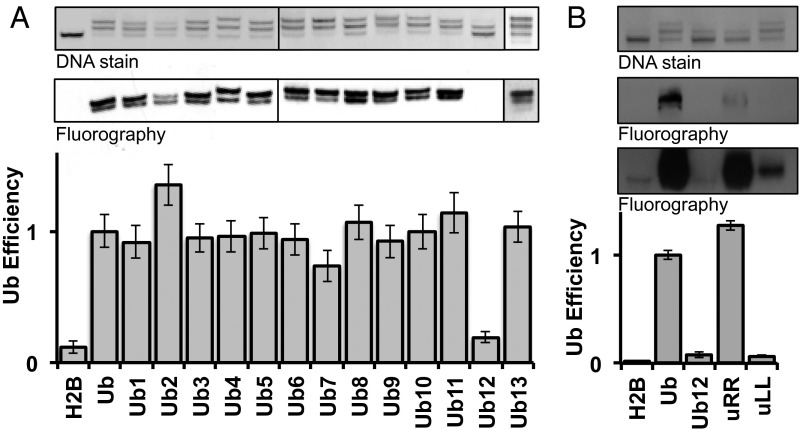
Fig. 3.
Surface features on ubiquitin critical for hDot1L stimulation. For all methyltransferase assays, nucleosomes were visualized by native PAGE followed by ethidium bromide staining (Top panels), and 3H-methyl incorporation was probed by fluorography (Middle panels). Quantification of methylation was performed by filter binding assays followed by liquid scintillation counting and was adjusted to include the extent of Ub-SH ligation, termed Ub efficiency (Bottom panels; see note in SI Appendix for details). Error bars, s.e.m. (n = 3–6). (A) hDot1L activity on each of the Ub surface mutants, 1–13. Nonubiquitylated nucleosomes (H2B) and wild-type ubiquitylated H2B nucleosomes (Ub) were included as negative and positive controls, respectively. Only the Ub7 and Ub12 mutants led to a significant reduction in hDot1L stimulation. The Ub13 mutant, centered on the canonical hydrophobic hotspot, did not lead to reduction in hDot1L activity, which is consistent with a previous study (see the Introduction). (B) Ub12 was split into two alanine submutants, uLL and uRR, and hDot1L activity was assayed via 3H-SAM methyltransferase assays. Middle panels show two different exposures of 12 h (Top Middle panel) and 5 d (Bottom Middle panel).