Table 1.
Optimization of the asymmetric α-amino radical additiona
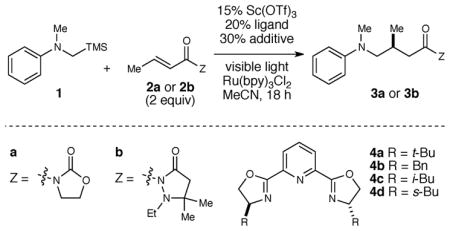
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | acceptor | ligand | [Ru] mol% | additive | yield (%)b | ee (%)c |
| 1d,e | 2a | none | 2% | none | 28 | -- |
| 2d | 2a | tBuPybox (4a) | 2% | none | 18 | 49 |
| 3d | 2a | BnPybox (4b) | 2% | none | 75 | 27 |
| 4d | 2a | iBuPybox (4c) | 2% | none | 15 | 42 |
| 5d | 2a | sBuPybox (4d) | 2% | none | 70 | 43 |
| 6 | 2a | sBuPybox (4d) | 2% | none | 94 | 50 |
| 7 | 2a | sBuPybox (4d) | 5% | none | 93 | 59 |
| 8 | 2a | sBuPybox (4d) | 15% | none | 97 | 66 |
| 9 | 2a | sBuPybox (4d) | 2% | KCl | 74 | 59 |
| 10 | 2a | sBuPybox (4d) | 2% | Bu4N+Cl− | 91 | 67 |
| 11 | 2a | sBuPybox (4d) | 2% | Bu4N+PF6− | 52 | 43 |
| 12 | 2a | sBuPybox (4d) | 2% | Bu4N+ClO4− | 40 | 46 |
| 13 | 2b | sBuPybox (4d) | 2% | Bu4N+Cl− | 80 | 89 |
| 14 | 2b | iBuPybox (4c) | 2% | Bu4N+Cl− | 83 | 93 |
| 15f | 2b | iBuPybox (4c) | 2% | Bu4N+Cl− | <5 | -- |
| 16e | 2b | none | 2% | Bu4N+Cl− | 52 | -- |
| 17 | 2b | iBuPybox (4c) | 0% | Bu4N+Cl− | 0 | -- |
| 18 | 2b | iBuPybox (4c) | 2% | none | 91 | 86 |
Unless otherwise noted, reactions were conducted at 0.05 M in 1 and irradiated at a distance of 30 cm from a 23 W compact fluorescent light bulb.
Yields determined by 1H NMR using an internal standard.
Enantiomeric excess determined by chiral SFC analysis.
Reaction conducted at 0.25 M in 1.
Reaction conducted without Lewis acid.
Reaction conducted with N,N-dimethyl amine in place of silyl amine 1.
