Figure 4.
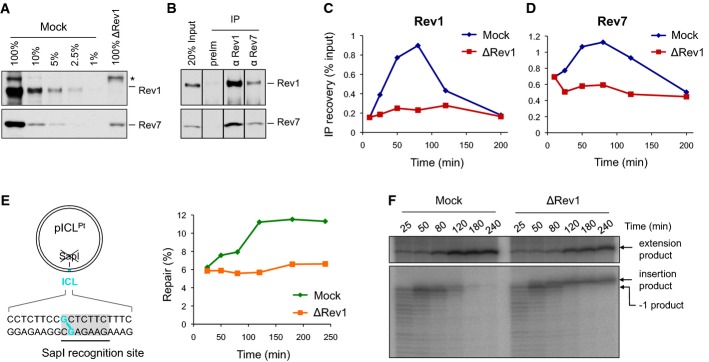
Rev1 depletion inhibits the extension step
- A Rev1-depleted NPE and a dilution series of mock-depleted NPE were analyzed by Western blotting using Rev1 and Rev7 antibodies. 100% corresponds to 0.25 μl of NPE.
- B Reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation of Rev1 and Rev7. 20% of input (0.8 μl of NPE) and proteins precipitated from 4 μl of NPE (IP) were blotted with Rev1 and Rev7. preIm, preimmune serum.
- C, D pICL was replicated in mock- or Rev1-depleted egg extracts. ChIP was performed with antibodies against Rev1 (C) and Rev7 (D) at the indicated time points. An experimental replicate of (D) is shown in Supplementary Fig S4A.
- E Left: cartoon of pICL indicating the SapI site that is blocked by the ICL. Right: DNA samples from pICL replication (performed in parallel with those shown in C and D) were cut with SapI, and repair efficiency was calculated as described (Knipscheer et al, 2012). The background level of SapI-cleavable products in the Rev1-depleted reaction is due to contamination of pICL by un-cross-linked plasmid (Knipscheer et al, 2009). The amount of SapI-cleavable products can vary between experiments due to differences in the amount of un-cross-linked plasmid and in the repair capacity of individual batches of extract.
- F Lesion bypass in mock- and Rev1-depleted extracts. DNA samples from (E) were cut with AflIII and analyzed on a denaturing gel, as described in Fig2B. A repetition of this experiment is shown in Supplementary Fig S4B.
Source data are available online for this figure.
