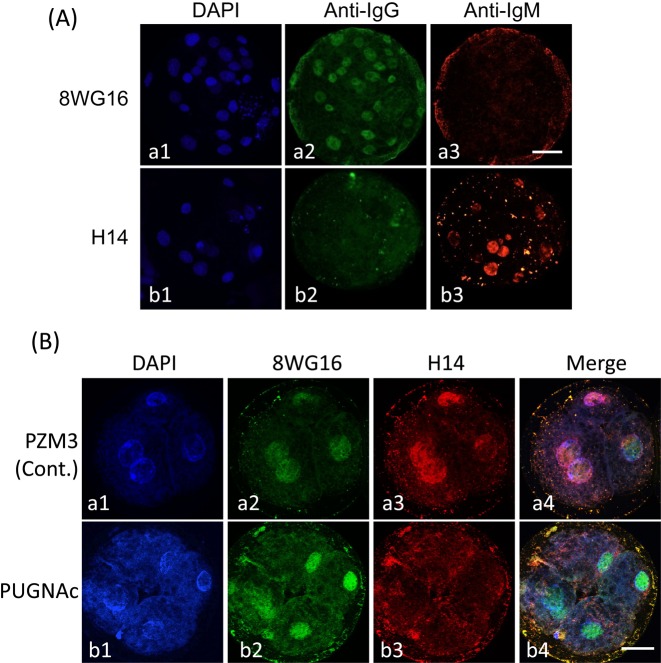
Fig. 7.
Localization of Pol II and phosphorylated Pol II (pPol II) in pig parthenogenetically activated diploids. (A) Cross-reactivity test between primary antibodies (8WG16 and H14) and secondary antibodies (anti-mouse IgG antibody labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 and anti-mouse IgM antibody labeled with Alexa Fluor 564). Blastocysts after culture of diploids for 144 h and treatment with 8WG16, which reacted with Pol II and phosphorylated Pol II (pPol II), and H14, which reacted with pPol II alone. Both primary antibodies were derived from primed mice; the immunoglobulin isotypes of 8WG16 and H14 were IgG and IgM, respectively. Therefore, it had to be confirmed that only pPol II was detected by H14 when diploids were subjected to double immunofluorostaining using these primary and secondary antibodies. The anti-mouse IgG antibody labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 reacted with 8WG16 (a2); but not H14 (b2), while the anti-mouse IgM labeled with Alexa Fluor 564 reacted with H14 (b3); but not 8WG16 (a3). Diploids were observed under an epifluorescence microscope. (B) Localization of Pol II and pPol II in pig parthenogenetically activated diploids exposed to PUGNAc. Diploids were cultured in PZM3 containing 0 (control) and 300 µM PUGNAc from 4 to 48 h after electrostimulation. Four-cell diploids were treated with 8WG16 and H14 and then stained with Alexa Fluor 488 and Alexa Fluor 564 labeled secondary antibodies. Pol II is shown by green (a2 and b2), and pPol II is shown by red (a3 and b3). All diploids were counterstained with DAPI (blue; a1 and b1). Merged images are shown in the right column (a4 and b4). Pol II was detected in nuclei in both groups (a2 and b2), whereas pPol II was only detected in nuclei in the control group (a3). Diploids were observed under a confocal laser microscope. Scale bar = 50 µm.