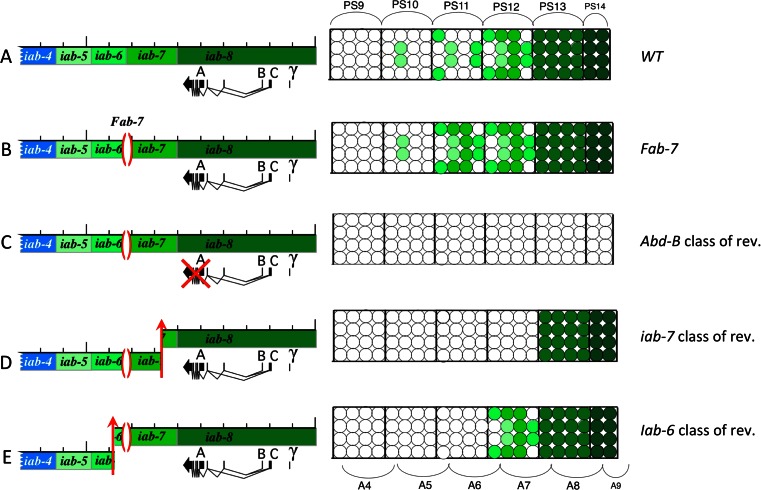
Fig. 4.
Fab-7 mutation and revertants. The Abd-B transcription unit and associated regulatory domains iab-5 through iab-8 are drawn on the left of each panel. The parasegment-specific expression pattern of Abd-B are represented on the right in the form of cartoon of the central nervous system (with parasegmental and segmental borders indicated respectively above and below). In WT, panel a, Abd-B is expressed at a low level in a few cells in PS10. This expression is controlled by the iab-5 regulatory domain. In PS11, a few more cells express Abd-B at a slightly higher level, under the control of iab-6. In PS12 additional cells express Abd-B at a higher level, under the control of the iab-7 domain. Finally, in PS13, Abd-B appears in all cells at a higher level, under the control of iab-8. It should be noticed that in PS14, a truncated form of Abd-B is expressed from alternate promoters (B, C, and γ) at even a higher level. The enhancers controlling Abd-B expression in PS14 are not known. In panel b, the Fab-7 1deletion located between iab-6 and iab-7 is drawn on the genomic map. This deletion leads to the ectopic activation of iab-7 in PS11, resulting in the appearance of the PS12-specific Abd-B expression pattern in PS11. Panel c represents the first class of Fab-7 1 revertants that inactivate Abd-B. This class confirmed that Fab-7 1 affects Abd-B regulation. Panel d represents the second class of Fab-7 1 mutations that map within the iab-7 region. As the rearrangement breakpoints separate iab-5, iab-6, and part of iab-7 from their Abd-B target promoter, Abd-B expression is lost in PS10, PS11, and PS12. This class of revertants confirmed that Fab-7 1 is misregulating iab-7. Finally, the 3rd class of Fab-7 1 revertants in which a rearrangement breakpoint occurred in iab-6 is represented in panel e. Overall, this analysis established that the Fab-7 1 GOF phenotype appears only if the whole region from iab-6 to the Abd-B transcription is intact in cis