Fig. 8.
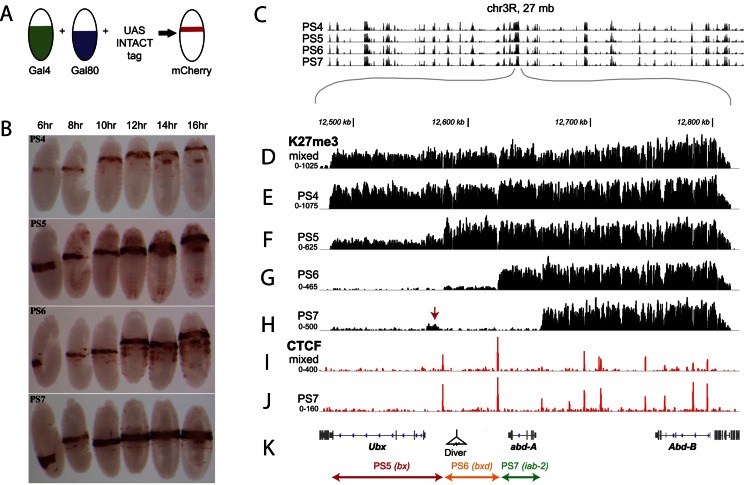
H3K27 modifications define segment-specific regulatory domains. The figure compiles Figs. 2 and 3 of Bowman et al. (2014); DOI 10.7554/eLife.02833 reproduced with the permission of eLife. Panel a shows the strategy to obtain strains expressing active yeast Gal4 activator in single parasegments. The homing fragment was used to attract transposons harboring either the Gal4 activator or the Gal80 repressor in the regulatory domains (see detailed procedure in figure supplement 1 of Bowman et al. 2014). Drivers for the Gal4 activator or the Gal80 repressors each with different anterior limit of expressions are combined by simple crosses (see also text). Panel b shows the resulting expression pattern for strains expressing active Gal4 in PS4, PS5, PS6, and PS7, respectively. Note the existence of weak leakiness in anterior parasegments in the PS5-specific combination (see remark below). These Gal4 strains active in single parasegments are then crossed to INTACT construct (Deal and Henikoff 2010) to purify nuclei from single parasegment and perform ChIP-seq experiments with antibodies recognizing H3K27me3 modification. Panel c is a control experiment revealing that the overall H3K27me3 profile over a region of 27 Mb centered around the BX-C is invariant in the nuclei isolated from PS4, PS5, PS6, and PS7. Panels d through h show the H3K27me3 profile over the entire BX-C. The H3K27me3 profile from whole embryo (panel d) does not differ from the profile obtained from PS4 nuclei (panel e) where the entire BX-C is repressed. In PS5 however (panel f), the H3K27me3 profile is greatly reduced over the PS5-specific regulatory domain (as indicated in k). The fact that the H3K27me3 profile does not reach the background levels seen in the more posterior domains (panel g and h) probably stems from the leakiness of the PS5 specific driver in anterior parasegments, suggesting that the preparation is contaminated with nuclei originating from anterior inactive regions. Note the progressive loss of H3K27me3 modifications in nuclei derived from PS6 and PS7 (panel g and h, respectively). Panels i and j show that the CTCF binding profiles do not differ in nuclei isolated from PS7 and mixed nuclei isolated from whole embryos, suggesting that this boundary factor is bound in a constitutive fashion, regardless of the state of activity of the regulatory domans of the BX-C