Table 4. Correlation of VOCs with replication time and molecular markers of breast-derived cell lines.
| Class | Compound | CDT | ER status | PgR status | HER2 status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >48 h vs ≤48 h | (−) vs (+) | (−) vs (+) | (−) vs (+) | ||
| Hydrocarbons | 2,4-Dimethyl-1-heptene | 2.9 × 10−4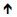
|
0.78 | 0.30 | 0.89 |
| 1,3-Di-tert-butylbenzene | 0.29 | 0.88 | 0.049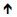
|
0.25 | |
| 2-Xylene | 0.14 | 6.2 × 10−4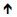
|
2.5 × 10−5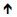
|
0.08 | |
| 2,3-Dimethylhexane | 8.4 × 10−5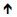
|
0.98 | 0.15 | 0.41 | |
| Secondary alcohol | Cyclohexanol | 0.001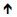
|
0.42 | 0.51 | 0.78 |
| Fatty alcohol | 2-Ethylhexanol | 1.9 × 10−6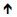
|
9.1 × 10−5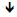
|
0.046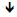
|
0.16 |
| Carboxylic acid | Isobutyric acid, allyl ester | 0.04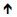
|
0.12 | 0.59 | 0.86 |
| Ketons | 2-Dodecanone | 0.009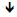
|
0.003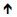
|
0.005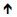
|
0.01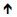
|
| 2-Nonanone | 0.11 | 0.001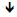
|
0.58 | 0.85 | |
| 4-Methyl-2-heptanone | 0.023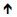
|
6.4 × 10−4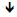
|
0.18 | 0.48 | |
| Manova | 5 × 10−4 | 3.5 × 10−5 | 7.4 × 10−4 | 0.03 |
Comparison of GC-MS results in all breast-derived cell lines grouped based on CDT, expression of ER, PgR and amplification of HER2. Arrows indicate the trend for each compound in each group. The p-values obtained by t-test analysis for each compound and by MANOVA analysis for all compounds reported in Table 2 are shown. A p-value < 0.05 has been considered statistically significant.
