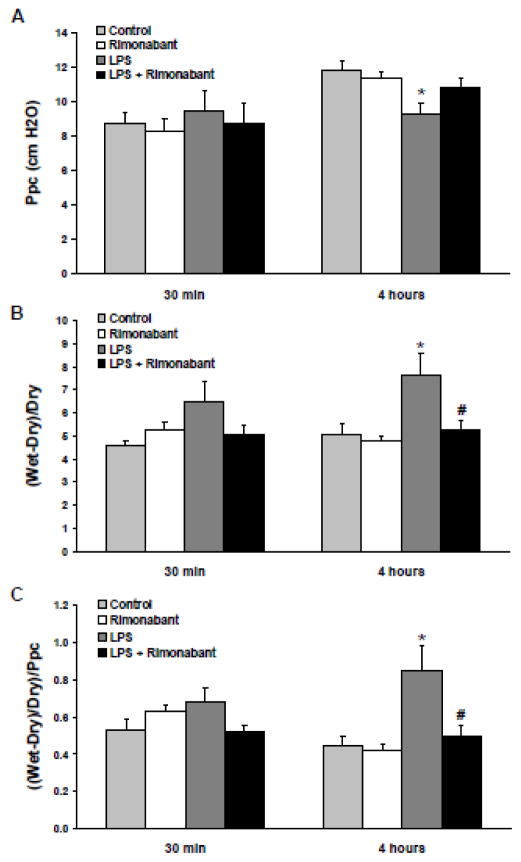
Figure 1. Rimonabant prevents the pulmonary hemodynamic changes and pulmonary fluid accumulation following systemic LPS.
Following a 30 minute or 4 hour exposure to 5mg/kg systemic LPS dose (IV) with or without intracerebroventricular rimonabant pre-treatment (500 ng in 0.5 μl saline + 2.5% DSMO), the lungs and heart of rats were excised and suspended from an isolated-lung apparatus, ventilated with room air, perfused with Ringer’s/BSA solution (pH 7.4), and maintained at 37 °C. A) The pulmonary artery and left atrial appendage were cannulated to measure pulmonary arterial pressure and to maintain pulmonary venous pressure at 2.9 mmHg, respectively. Pulmonary capillary pressure (Ppc) was estimated using the double occlusion method after 15 minutes of perfusion. B) Following the pulmonary hemodynamic measurements, the lungs were separated into left and right halves. Left lungs were weighed in their wet state and subsequently oven dried for three days. The left lung wet to dry weight ratio was calculated by ((wet weight – dry weight)/dry weight) ((W-D)/D). C) The (W-D)/D ratio of each lung was indexed to the Ppc obtained for that lung as ((W-D)/D)/Ppc. Data are mean ± S.E.M. Significance was at P<0.05. * = significantly different from respective control. # = significantly different from its LPS-only group.