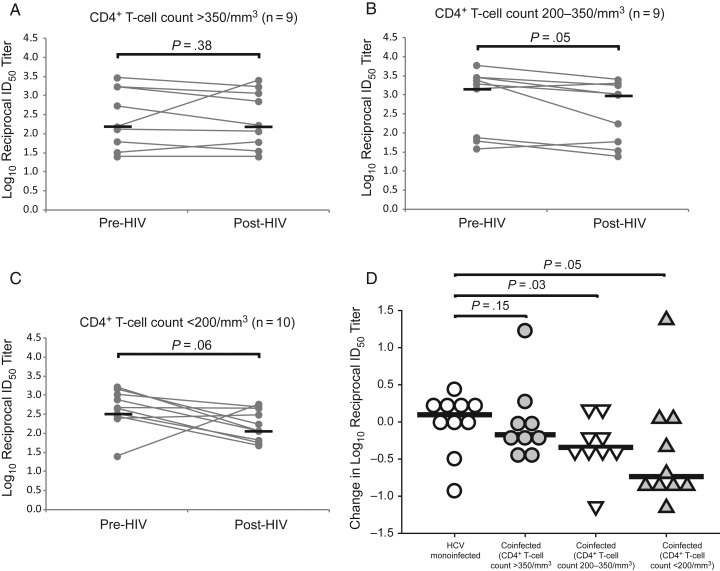
Figure 4.
Decline in anti–hepatitis C virus (HCV) neutralizing antibody (nAb) titers after incident human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection occurs in subjects with CD4+ T-cell loss. A–C, Anti-HCV nAb titers were stable after incident HIV infection in subjects with CD4+ T-cell counts >350/mm3, declined significantly in those with counts of 200–350/mm3, and trended downward in those with counts <200/mm3. Gray lines represents titers for individual subjects measured at 2 time points; black lines, medians. Any nAb titers below the level of detection were assigned a 50% inhibitory dose (ID50) value of 1:25 for comparison analysis. Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to calculate significance of changes; when normality was satisfied, paired t tests were used. D, Comparison of the change in nAb titers over time in HCV-monoinfected controls and HIV/HCV-coinfected subjects stratified by post-HIV CD4+ T-cell counts. Symbols represent changes for individual subjects; black lines indicate medians. Rank sum tests were used to calculate significance; when normality was satisfied, t tests were used.