Abstract
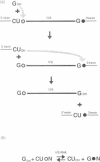
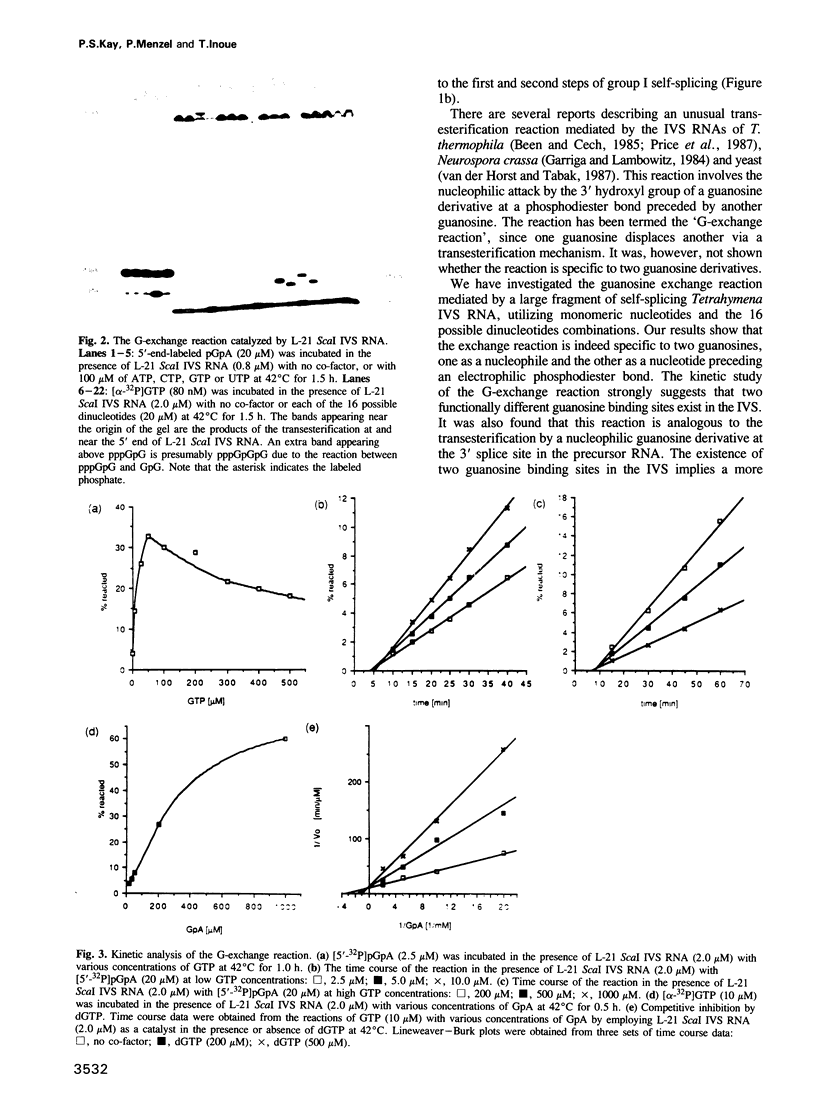
A shortened form of the self-splicing rRNA intervening sequence (IVS) of Tetrahymena thermophila can catalyze a transesterification reaction, termed G-exchange, between a monomeric guanosine derivative such as GTP and the substrate GpN (where N is A, C, G or U). The reaction is specific to the two guanosines involved, providing evidence that two guanosine binding sites exist in this group I IVS RNA. One binding site accommodates a guanosine which initiates self-splicing and the other recognizes the guanosine preceding the 3' splice site. Previously, only one guanosine binding site was thought to be involved in the mechanism of self-splicing. Based on the two functionally distinguishable guanosine binding sites, a new model is proposed to explain how the two independent transesterification reactions required for self-splicing might proceed in a concerted manner.
Full text
PDF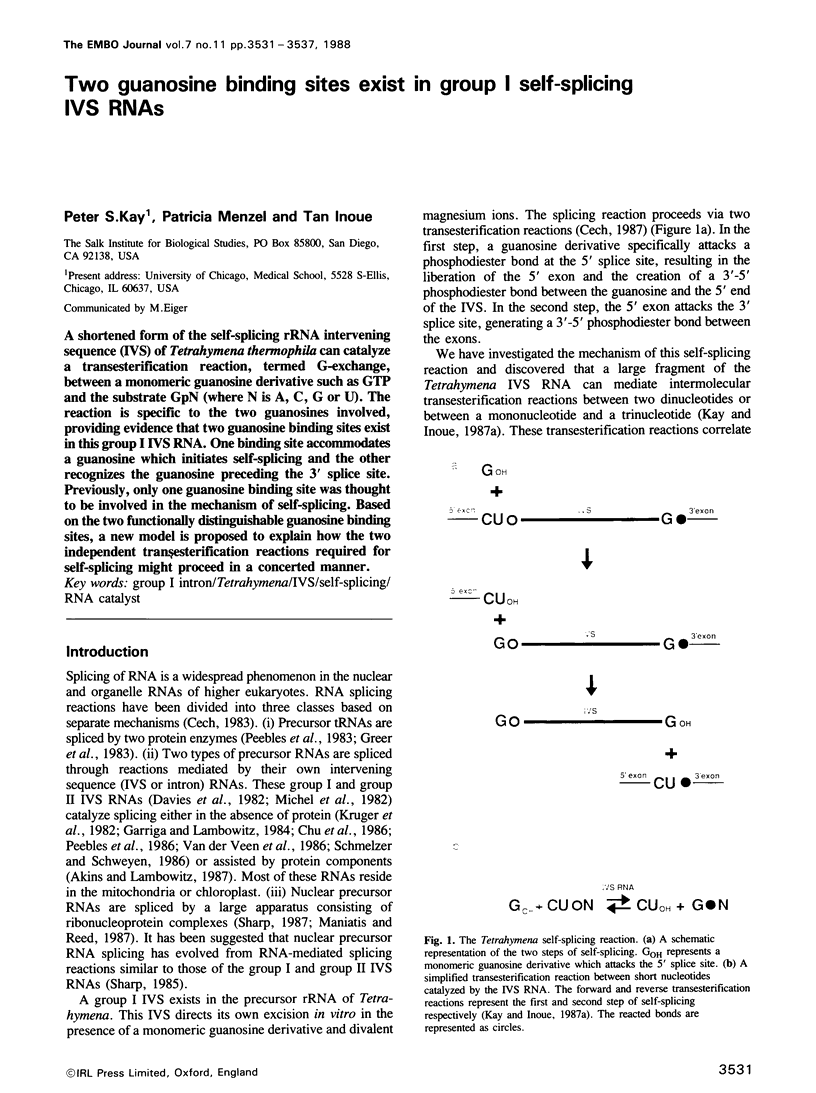




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M. A protein required for splicing group I introns in Neurospora mitochondria is mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase or a derivative thereof. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barfod E. T., Cech T. R. Deletion of nonconserved helices near the 3' end of the rRNA intron of Tetrahymena thermophila alters self-splicing but not core catalytic activity. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):652–663. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass B. L., Cech T. R. Ribozyme inhibitors: deoxyguanosine and dideoxyguanosine are competitive inhibitors of self-splicing of the Tetrahymena ribosomal ribonucleic acid precursor. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4473–4477. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass B. L., Cech T. R. Specific interaction between the self-splicing RNA of Tetrahymena and its guanosine substrate: implications for biological catalysis by RNA. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):820–826. doi: 10.1038/308820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. One binding site determines sequence specificity of Tetrahymena pre-rRNA self-splicing, trans-splicing, and RNA enzyme activity. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. Selection of circularization sites in a group I IVS RNA requires multiple alignments of an internal template-like sequence. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90522-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Cech T. R. Sites of circularization of the Tetrahymena rRNA IVS are determined by sequence and influenced by position and secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8389–8408. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. RNA splicing: three themes with variations. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90527-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The chemistry of self-splicing RNA and RNA enzymes. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1532–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.2438771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Maley G. F., West D. K., Belfort M., Maley F. Characterization of the intron in the phage T4 thymidylate synthase gene and evidence for its self-excision from the primary transcript. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific labeling of 3' termini of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriga G., Lambowitz A. M. RNA splicing in neurospora mitochondria: self-splicing of a mitochondrial intron in vitro. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer C. L., Peebles C. L., Gegenheimer P., Abelson J. Mechanism of action of a yeast RNA ligase in tRNA splicing. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90473-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sullivan F. X., Cech T. R. New reactions of the ribosomal RNA precursor of Tetrahymena and the mechanism of self-splicing. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):143–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay P. S., Inoue T. Catalysis of splicing-related reactions between dinucleotides by a ribozyme. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):343–346. doi: 10.1038/327343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay P. S., Inoue T. Reactivity of modified ribose moieties of guanosine: new cleavage reactions mediated by the IVS of Tetrahymena precursor rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1559–1577. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger K., Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Sands J., Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Gegenheimer P., Abelson J. Precise excision of intervening sequences from precursor tRNAs by a membrane-associated yeast endonuclease. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90472-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Perlman P. S., Mecklenburg K. L., Petrillo M. L., Tabor J. H., Jarrell K. A., Cheng H. L. A self-splicing RNA excises an intron lariat. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J. V., Engberg J., Cech T. R. 5' exon requirement for self-splicing of the Tetrahymena thermophila pre-ribosomal RNA and identification of a cryptic 5' splice site in the 3' exon. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90510-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schweyen R. J. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: mapping of the branch point and mutational inhibition of lariat formation. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. On the origin of RNA splicing and introns. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Been M. D., Cech T. R. The Tetrahymena ribozyme acts like an RNA restriction endonuclease. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):429–433. doi: 10.1038/324429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. The intervening sequence RNA of Tetrahymena is an enzyme. Science. 1986 Jan 31;231(4737):470–475. doi: 10.1126/science.3941911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Grabowski P. J., Cech T. R. Autocatalytic cyclization of an excised intervening sequence RNA is a cleavage-ligation reaction. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):578–583. doi: 10.1038/301578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Horst G., Tabak H. F. New RNA-mediated reactions by yeast mitochondrial group I introns. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2139–2144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., van der Horst G., Bonen L., Tabak H. F., Grivell L. A. Excised group II introns in yeast mitochondria are lariats and can be formed by self-splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]