Fig. 3.
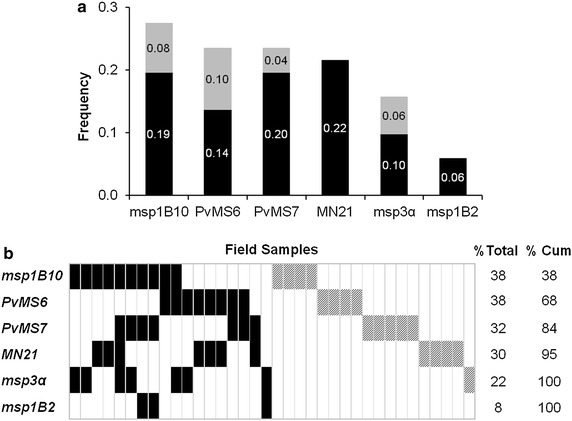
Detection of multiple-clone infections in field samples. The six markers were genotyped in 51 samples from malaria-endemic area of Brazil. A cut-off value of one-fourth was considered for the analysis. a The frequency of multi-clonal infections was calculated considering both criteria for minor allele detection: a cut-off value of one-third (black bars only) or one-fourth (the entire bar, including both black and grey bars) of the height of the predominant peak. The increase in the rate of detection of multiple-clone infections with the one-fourth criterion is highlighted in grey. b Results of genotyping are shown for the 36 samples with multiple-clone infection detected by one (hatched rectangles) or more markers (rectangles colored in black). Each column represents the same sample genotyped with the six markers. The frequency of multi-clonal infections (% Total) was calculated for each marker. The increase in the number of multiple-clone infections detected, resulting from the combination of two or more markers, is indicated as the cumulative percentage (% Cum)
