Figure 2.
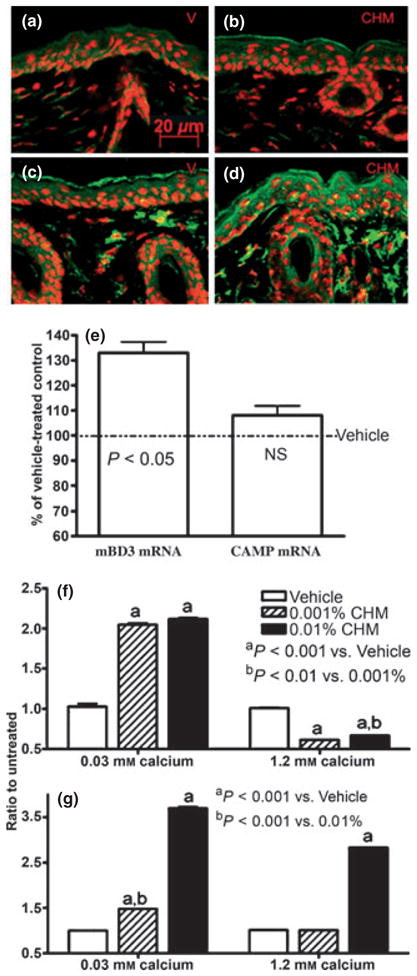
Topical Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) extract increases epidermal CAMP and mBD3 expressions in murine skin. Skin samples were from mice treated with either vehicle alone (a, c) or CHM extract (b, d) twice daily for 7 days. Five micrometers sections were incubated with the primary antibodies (1:500 dilutions) overnight at 4°C. After washing, sections were incubated with the secondary antibody for 30 min. Sections were examined with a Zeiss fluorescence confocal microscope, and digital images were captured with AxioVision software (Carl Zeiss Vision, Munich, Germany). Immunofluorescent staining (green color) for mouse b-defensin 3 (mBD3) (a, b), cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) (c, d). (a, c) Vehicle-treated and (b, d) CHM-treated. Propidium iodide was used for counterstaining. Scale bars represent 20 μm (a–d). (e) Changes in epidermal CAMP and mBD3 mRNA expressions over vehicle. Data are expressed as % of vehicle-treated control (n = 4 for both). (f, g) LL-37 and human β-defensin 2 mRNA expressions in keratinocytes (from foreskin), respectively. Second-passage human keratinocytes cultured in 0.3 or 1.2 mM calcium were treated with either 0.01%, 0.001% herbal extract or vehicle for 36 h. Total RNA was extracted with a commercial kit (RNeasy RNA isolation kit; Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. mRNA expressions were assessed as described in Experimental design section. Samples were run in triplicate, and results were normalized to untreated group (n = 3).
