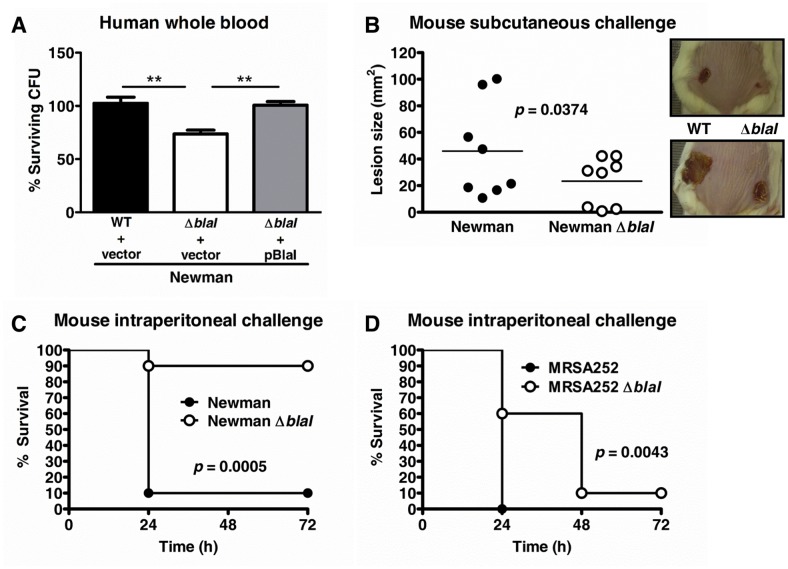
Fig 3. BlaI contributes to survival in human whole blood and virulence in vivo.
(A) S. aureus Newman WT with empty complementation vector pDC123, the blaI mutant with pDC123, and the complemented blaI mutant strain were incubated for 1 h in human whole blood and CFU numbers enumerated. Samples were run in triplicate and data were plotted as the average percentage ± SD for each strain as compared to the initial inocula. A representative experiment of three performed is shown. **, p<0.01. (B) CD-1 mice (n = 8) were injected subcutaneously on one flank with S. aureus Newman WT and on the opposite flank with blaI mutant bacteria, and lesion sizes were monitored for 7 days. The lesions for each individual mouse at Day 7 are plotted and the average value indicated. Overall, the blaI mutant lesions were significantly smaller compared to the WT (p<0.04; paired t-test). (C-D) Survival of CD-1 mice (n = 10) after intraperitoneal infection with (C) 1 x 106 CFU of S. aureus Newman WT or Newman blaI mutant or (D) 6 x 108 CFU of MRSA252 or MRSA252 blaI mutant. Survival was monitored for 3 days. The survival for Newman or MRSA252 blaI mutant strain infected mice was significantly higher than for the WT infected strains as assessed by log-rank (Mantel Cox) test; the p values are shown in the respective graphs.