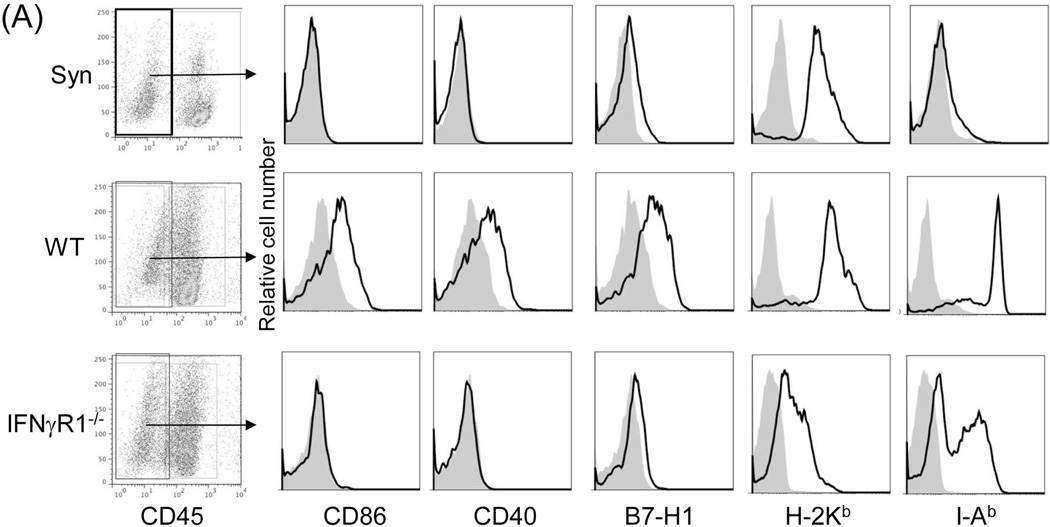
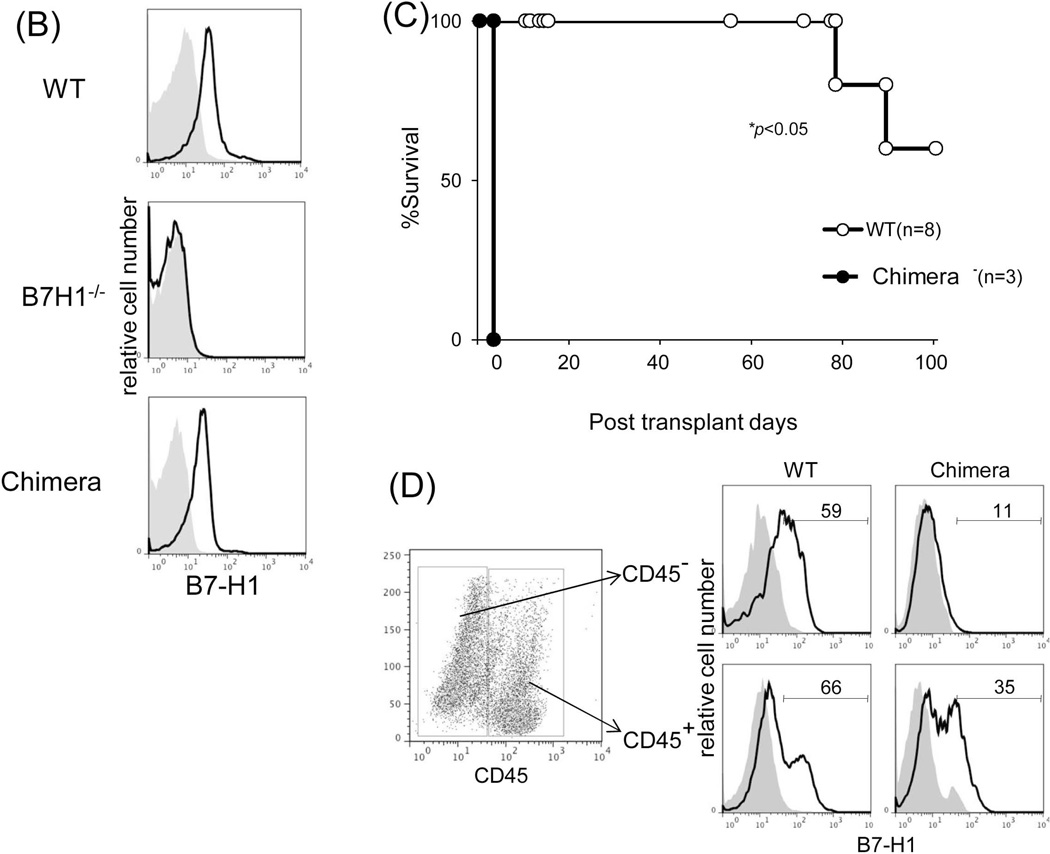
Figure 4. B7-H1 mediates the immune regulatory function of graft non-hematopoietic NPC.
(A) Expression of key surface molecules on graft non-hematopoietic NPC. Expression of CD40, CD86, B7-H1, MHC class I and II was analyzed by flow cytometry gated on CD45− NPC that were isolated from WT or IFN-γR1−/− liver allograft on POD 12, expressed as histograms. Syngeneic graft (Syn) served as control. The shaded area is isotype control. (B) Establishment of chimeras. Transplantation of BM from WT B6 into lethally irradiated B7-H1−/− mice as described in the Methods section. Five weeks later, chimeric status was examined by determining expression of B7-H1 on peripheral blood cells by flow cytometry, expressed as histograms. Blood from naïve WT B6 or B7-H1−/− mice served as controls. (C) Liver transplant tolerance requires B7-H1 expression on graft non-hematopoietic NPC. The liver from chimeric (n=3) or WT mice (n=8) was transplanted into WT C3H recipients. Graft survival was compared. (D) Expression of B7-H1 on NPC of liver allografts. NPC were isolated from chimeric or WT liver allografts on POD 5. Expression of B7-H1 was analyzed gated on CD45+ and CD45− cells, respectively, expressed as histograms. The shaded area is isotype control. The number is the percentage of positive cells. The data are representative of three separate experiments.