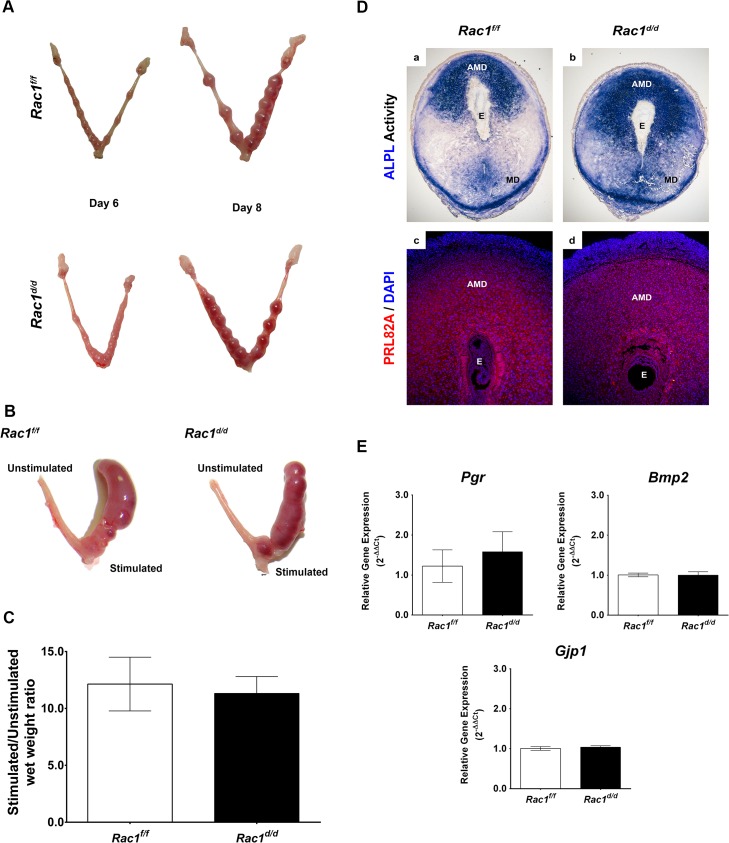
Fig 3. Early implantation is unaffected in Rac1 conditional knockout mouse.
(A) Gross morphology of Rac1f/f and Rac1d/d uteri at days 6 and 8 of gestation. (B) Rac1f/f and Rac1d/d mice were subjected to artificial decidual stimulation for 96 hours as described in the Materials and methods. For each mouse, one uterine horn was stimulated, while the other horn was left undisturbed. Gross morphology of Rac1f/f and Rac1d/d uteri following the application of the decidual stimulus is shown. (C) Comparative wet weight gains in uteri of Rac1f/f and Rac1d/d mice. Following artificial decidualization, stimulated and unstimulated horns were assessed for wet weight gain. The histogram shows the ratios of average weights of stimulated over unstimulated horns from Rac1f/f and Rac1d/d mice. Data represent mean ± SEM from four separate samples and were analyzed by t-test, P > 0.05). (D) Uterine sections from Rac1f/f and Rac1d/d mice on day 8 of pregnancy were subjected to alkaline phosphatase activity (ALPL, upper) and IF staining using an antibody specific for the prolactin-related protein (PRL82A, lower). AMD, MD, and E denote antimesometrial decidua, mesometrial decidua, and embryo respectively. (E) Comparable expressions of various markers of decidualization in Rac1f/f and Rac1d/d uteri. Total RNA was isolated from uteri on day 8 of pregnancy and qPCR analysis was performed using primers specific for Pgr, Bmp2, and Gja1. Data represent mean ± SEM from four separate samples and were analyzed by t-test, P > 0.05).