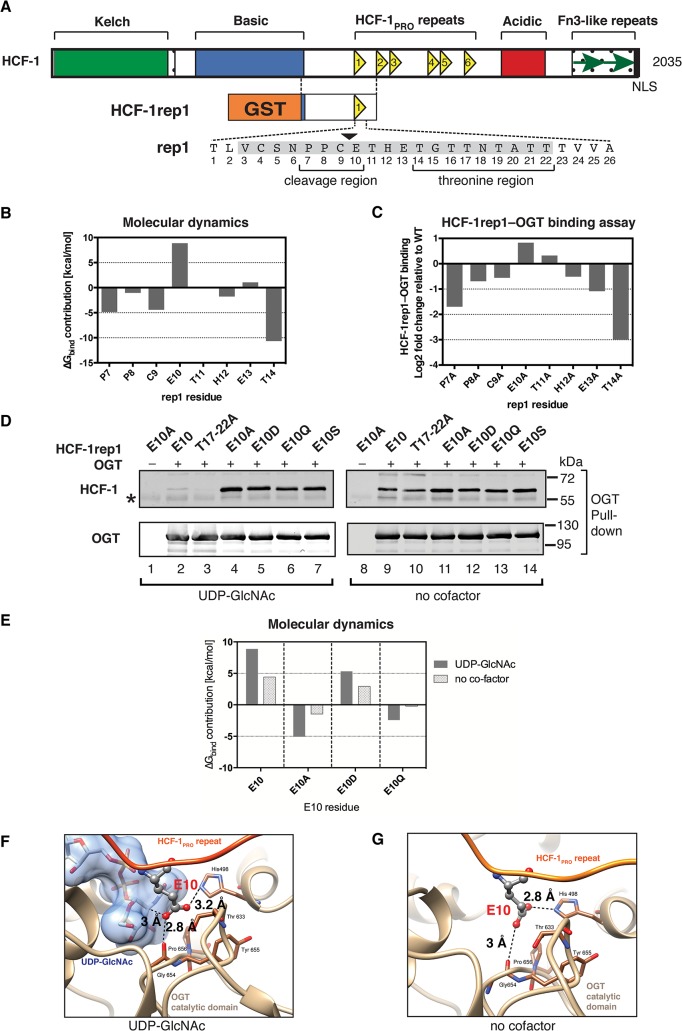
Fig 1. The glutamate residue at position 10 in the HCF-1PRO repeat inhibits OGT binding.
(A) (Top) Schematic representation of the human HCF-1 protein showing the six HCF-1PRO repeats as yellow triangles. (Bottom) Schematic of the recombinant HCF-1rep1 precursor (HCF-1 residues 867–1071), containing the HCF-1PRO repeat 1 (rep1) and surrounding sequences fused to glutathione-S-transferase (GST). The 26 residues of rep1 are shown and the site of proteolysis is marked at the C/E sequence by a black arrowhead. The 20 amino acid core sequence [14] is shaded gray, and the cleavage and threonine regions are indicated. (B) E10 exhibits inhibitory contributions to OGT binding. Computational estimation of the contributions to the binding free-energy, ΔG bind, of single amino acid residues in the HCF-1PRO repeat (P7-T14) for the association with OGT. Negative and positive values correspond to favorable and unfavorable OGT-association contributions, respectively, in the in silico structural complex (based on the 4N3B structure [22]). (C) An E10 to alanine substitution enhances HCF-1PRO-repeat–OGT binding. In vitro HCF-1rep1–OGT binding assay in the presence of UDP-GlcNAc with HCF-1rep1 constructs containing individual alanine substitutions in the HCF-1PRO repeat (P7A-T14A). HCF-1rep1 binding to OGT was quantified from an immunoblot (S1B Fig) as ratio of OGT-bound HCF-1rep1 to total HCF-1rep1 in the assay. Obtained values are presented as log2 fold change relative to wild-type HCF-1rep1–OGT binding. (D) HCF-1PRO-repeat–OGT binding is influenced by the E10 side-chain properties and exhibits sensitivity to UDP-GlcNAc. In vitro HCF-1rep1–OGT binding assay. Constructs with wild-type (WT), E10 missense mutations (E10A, E10D, E10Q, and E10S), and T17-T22A mutations were incubated in the presence (left panel) or absence (right panel) of UDP-GlcNAc. Detection of OGT and HCF-1rep1 was performed using the indicated antibodies. *, IgG heavy chain. (E) Computational estimation of the contributions to the binding free-energy, ΔG bind, of single amino acid residues at the E10 cleavage site for the association with OGT. Shown are residue contributions of WT (E10), alanine (E10A), aspartate (E10D) or glutamine (E10Q) side-chains in the presence or absence of UDP-GlcNAc in the in silico structural complex (based on the 4N3B structure). (F) Close-up view (4N3C crystal structure [22]) of the OGT active site with the HCF-1PRO repeat and UDP-GlcNAc. The deprotonated E10 oxygen atom exhibits an unfavorable interaction with OGT. (G) Snapshot from a molecular dynamics simulation (based on the 4N3B structure) of the OGT active site in complex with the HCF-1PRO repeat without UDP-GlcNAc. The displayed frame is representative of the average distances sampled along the simulations. In (F) and (G), the E10 side-chain is shown in ball and stick representation (carbons: gray, nitrogen: blue, oxygens: red), and dashed lines indicate distances between atoms.