Figure 5.
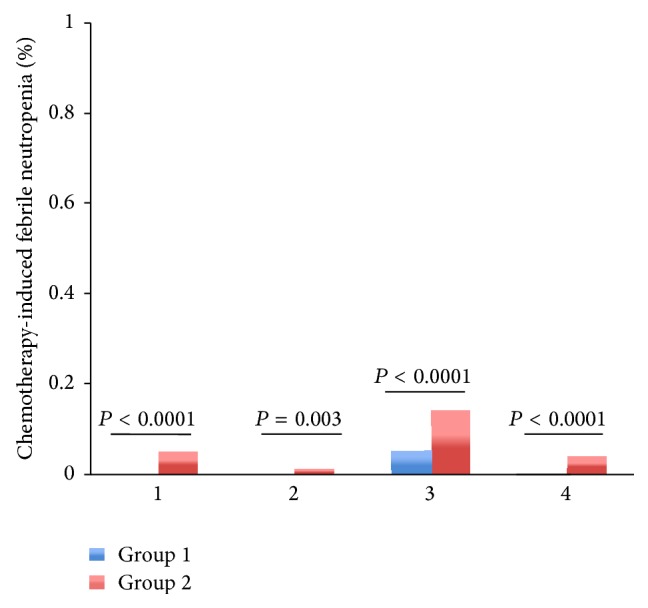
The rates of chemotherapy-induced FN for the entire propensity-matched patients in different chemotherapy regimens. After matching, patients in group 2 had a significantly higher rate of FN compared to patients in group 1 (5% versus 0%, P < 0.0001; 1% versus 0%, P = 0.003; 14% versus 5%, P < 0.0001; 4% versus 0%, P < 0.0001, resp.). Chemotherapy: 1: the chemotherapy regimens contain AC/EC (Adriamycin or epirubicin, Cyclophosphamide) and CAF/CEF (Adriamycin or epirubicin, Cyclophosphamide, and 5-Fluorouracil). 2: the chemotherapy regimens contain TC (paclitaxel or docetaxel, Cyclophosphamide) and T (paclitaxel or docetaxel). 3: the chemotherapy regimens contain anthracyclines combined with paclitaxel or docetaxel: TAC/TEC (paclitaxel or docetaxel, Cyclophosphamide, and Adriamycin or epirubicin); TA/TE (paclitaxel or docetaxel, Adriamycin or epirubicin). 4: the chemotherapy regimens contain anthracyclines followed by paclitaxel or docetaxel: AC/EC (Adriamycin or epirubicin, Cyclophosphamide); CAF/CEF (Adriamycin or epirubicin, Cyclophosphamide, and 5-Fluorouracil), followed with T or TH (paclitaxel or docetaxel, Herceptin).
