Figure 2.
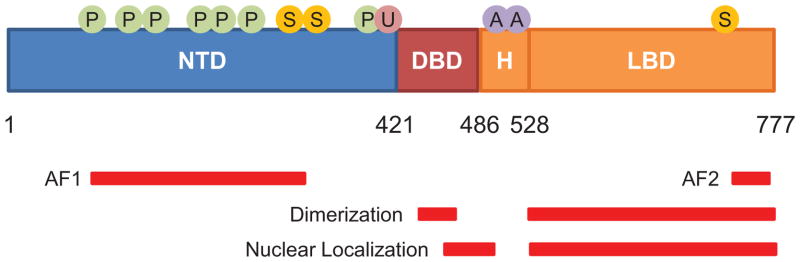
GR structural domains and sites of posttranslational modification. Numbers indicate position of amino acid residues in human GR. The N-terminal transactivation domain (NTD), DNA-binding domain (DBD), hinge region (H), and ligand-binding domain (LBD) for GR are shown. Regions associated with transactivation (AF1 and AF2), receptor dimerization, and nuclear localization are shown by red bars. Also shown are residues subject to translational modification by phosphorylation (P), sumoylation (S), ubiquitination (U), and acetylation (A).
