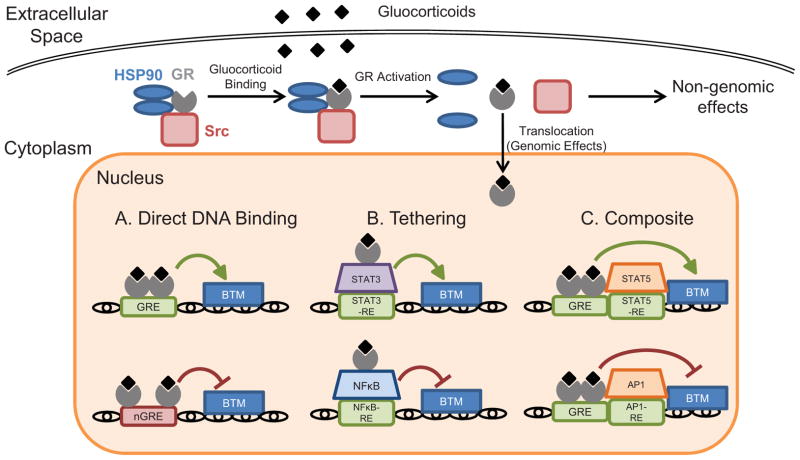
Figure 3.
Pathways of glucocorticoid signaling through the GR. GR ligands induce biological changes by binding the GR and inducing genomic and non-genomic effects. Genomic effects of activated GR occur following nuclear translocation and manifest through 3 primary mechanisms: direct binding of GR to DNA via GREs and nGREs to activate or repress transcription (A), tethering to DNA-bound transcription factors to modulate transcription indirectly (B), or composite activity of DNA binding and interaction with adjacent DNA-bound transcription factors to affect transcription (C). Rapid non-genomic effects of GR ligation occur following ligand-induced dissociation of the GR multiprotein complex in the cytoplasm. BTM, basal transcription machinery.