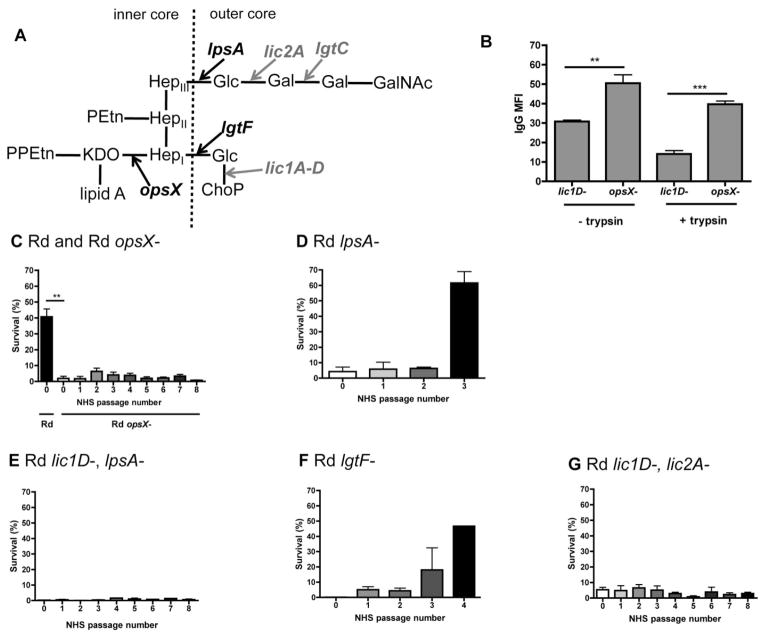
Fig. 1.
LPS structural requirements for resistance to human serum in the strain Rd. LPS structure proposed for Rd (Hood et al., 2001b), with arrows indicating extensions dependent on LPS biosynthesis genes (black, bold), or phase variable genes (grey, bold), and dashed line indicating the border between inner and outer core LPS structures (A). Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for binding of purified human IgG to the surface of the Rd lic1D– strain compared with the opsX– mutant, with or without trypsin digestion (B). Bactericidal assays, where survival in human serum is determined relative to controls with the same serum heat-inactivated to eliminate complement activity. Survival following serial passage in human serum is indicated for Rd and Rd mutants (C–G) in 3% normal human serum (NHS). Data shown are means and SEM (representative experiment in triplicate shown for D–G). Statistical analysis (n ≥ 3) was performed by an unpaired t-test; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.