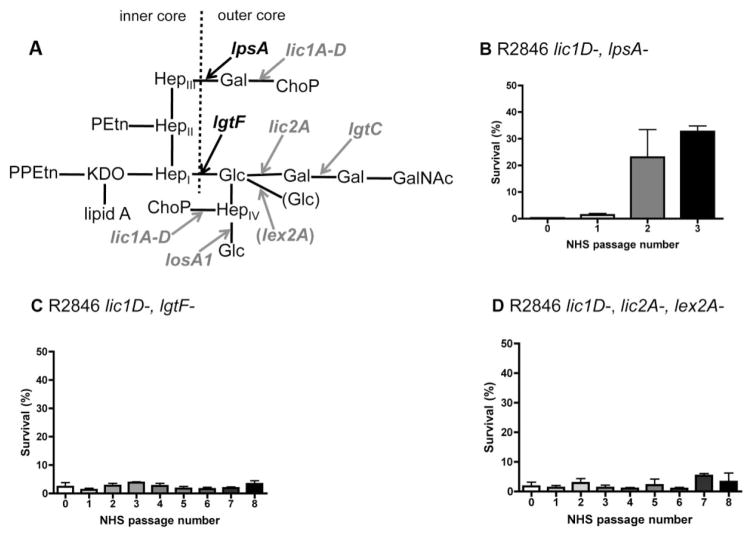
Fig. 2.
LPS structural requirements for resistance to human serum in the strain R2846. LPS structure proposed for NTHi clinical isolate R2846 (Lundstrom et al., 2008), with arrows indicating extensions dependent on LPS biosynthesis genes (black, bold), or phase variable genes (grey, bold), and dashed line indicating the border between inner and outer core LPS structures (A). Also included in parentheses is the phase variable gene responsible for the proposed alternative glucose extension (grey, bold), which can be attached to the same hexose moiety as the di-galactoside. Bactericidal assays for serial passage in 5% normal human serum (NHS), with survival following serial passage in human serum, for R2846 mutants (B–D). Data shown are means and SEM (representative experiments in triplicate).