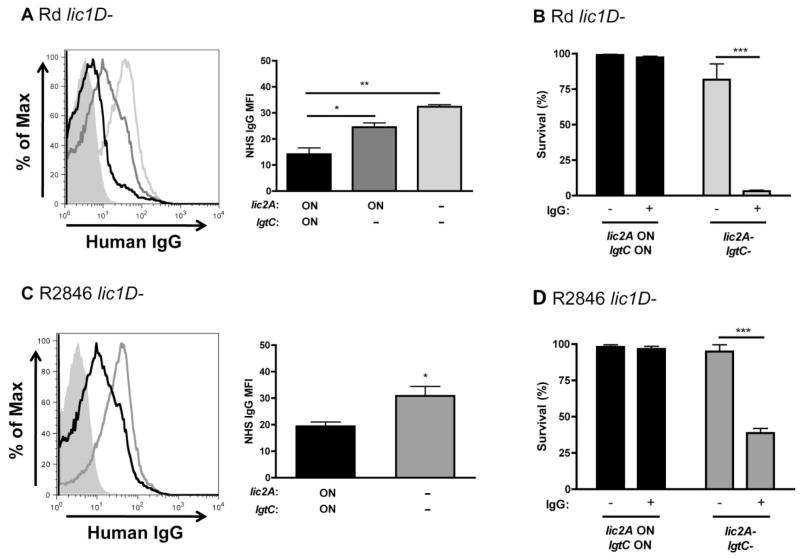
Fig. 5.
Di-galactoside expression protects against human IgG binding and bactericidal activity. Histogram of purified human IgG binding to lic2A and lgtC phase-on variants (black), a lic2A phase-on, lgtC– mutant (dark grey) and a lic2A– mutant (light grey) in Rd lic1D– (A). Graphical summary of IgG mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is also shown. Bactericidal assays in IgG-depleted human serum with or without purified human IgG added back, as indicated, for lic2A and lgtC phase-on variants and lic2A– mutants in Rd lic1D– (B, 2% IgG-depleted normal human serum, NHS). Histogram of purified human IgG binding to lic2A and lgtC phase-on variants (black) and a lic2A– mutant (grey) of R2846 lic1D– (C), with a graphical summary of IgG MFI. Bactericidal assays in IgG-depleted human serum with or without purified IgG added back, as indicated, for lic2A and lgtC phase-on variants and lic2A– mutants in R2846 lic1D– (D, 4% IgG-depleted NHS). Data shown are means and SEM. Statistical analysis (n ≥ 3) was performed by an unpaired t-test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.