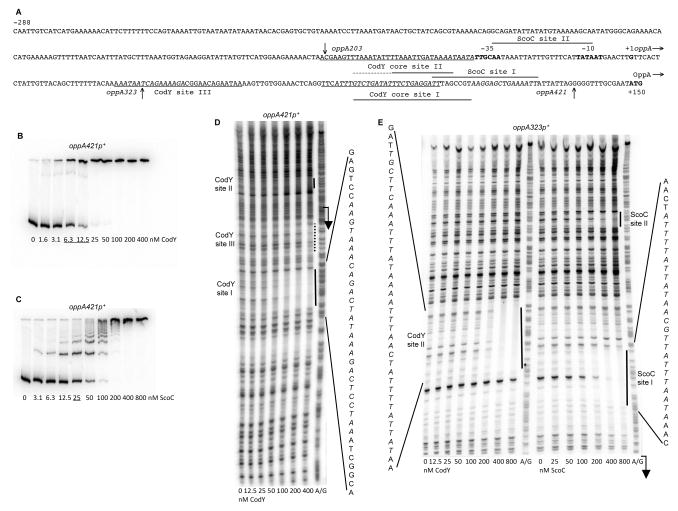
Fig. 4.
Binding of CodY and ScoC to the oppA regulatory region.
A. The sequence (5’ to 3’) of the coding (non-template) strand of the oppA regulatory region. Coordinates are reported with respect to the transcription start point (Irnov et al., 2010). The 5’ nucleotide of the sequence presented corresponds to the first nucleotide of the oppA insert within the oppA421- and oppA323-lacZ fusions. The vertical arrow above the sequence indicates the 5’ nucleotide of the oppA203-lacZ fusion at position −69. The vertical arrows below the sequence indicate the junction points, at positions +36 and +134, between the oppA and lacZ sequences for the oppA323 or oppA421 and oppA203 fusions, respectively. The likely translation initiation codon (ATG), −10 and −35 promoter regions, and transcription start point are in bold. The directions of transcription and translation are indicated by the horizontal arrows. The sequences protected by CodY in DNase I footprinting experiments on the template strand of DNA are underlined. The core CodY-binding sites I and II identified by IDAP-Seq (Fig. 2B and 2C) and ScoC-binding sites determined by footprinting are shown by horizontal lines below the sequence; the 5’ boundary of the core site II is unknown. The CodY-binding motifs overlapping sites I and II and the ScoC-binding motif within site I are italicized; other CodY-binding motifs with 4 and 5 mismatches to the consensus can be found in the promoter region and are not shown.
B and C. Gel shift assays of protein binding to a radioactively labeled oppA421p+ PCR fragment, obtained with oligonucleotides oBB67 and oBB102. The proteins tested were (B) CodY in the presence of 10 mM ILV and (C) ScoC. Protein concentrations used (nM of monomer) are reported below each lane; concentrations corresponding to the apparent KD for binding are underlined.
D and E. DNase I footprinting analysis of protein binding to the oppA regulatory region. The oppA421p+ (D) or oppA323p+ (E) DNA fragment, obtained with oligonucleotides oBB67 and oBB102 and labeled on the template strand, was incubated with increasing amounts of (D and E) CodY in the presence of 10 mM ILV or (E) ScoC and then treated with DNase I. See the legend to Fig. 1E for additional details.