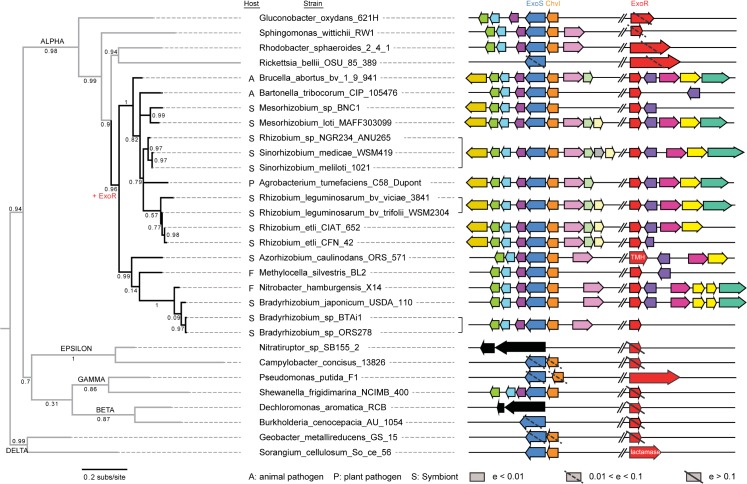
Fig 5. RSI Synteny analysis within Rhizobiales and ancestral Alphaproteobacteria.
Clusters of orthologous gene (COG) groups for representative Proteobacteria are presented for comparison to the prototype, the loci of Rm1021. Each COG, as defined in the IMG database, is represented by an arrow of different color. For the exoR-exoS-chvI genes, a lack of homologs or orthologs is presented as an ORF with a solid or dotted slash, respectively. The sizes and positions of the ORFs are approximate, representing relative expansions/deletions. The ExoR ortholog found in Azorhizobium caulinodans, although annotated as an exopolysaccharide regulator, is predicted to encode transmembrane helices and is a structural outlier as compared to ExoR-like molecules found in other Rhizobiales. Lifestyles and host type are given by A (animal pathogen), P (plant pathogen), or S (symbionts). Gene loss/gain is indicated with-/+, respectively. COG# color key (L to R): Dark yellow, 0499; green, 1925; light blue, 2893; dark violet, 1493; blue (exoS/chvG), 0642; orange (chvI), 0745; light violet, 1866; pale green, 1186; grey, 1652; white, 3145; red (exoR), 0790; purple, 0708; magenta, 1502; bright yellow, 0232; turquoise (sporulation-domain encoding). In Rm1021 RSI loci are exoS (bp49252–51039), chvI (51419–52141), and exoR (1637310–1638116) on the SMc chromosome.