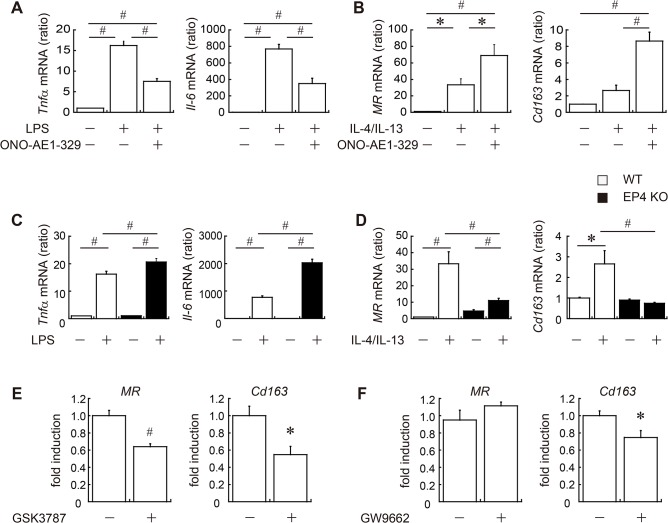
Fig 6. EP4 signaling is important in macrophage polarization.
In vitro M1/M2 polarization assays were performed using peritoneal macrophages freshly isolated from 12 to 15-week-old male WT (white bar) or EP4-deficient mice (black bar). To determine M1 or M2 polarization, cells were incubated with 1 μg/ml of LPS (A, C), or with 20 ng/ml of IL-4 and IL-13 (B, D), as well as with 1 μM of EP4 agonist or vehicle. Eight hours later, marker gene expression for M1 (Tnfα and Il-6) (A, C) or M2 (MR and Cd163) (B, D) polarity was measured. To clarify the role of PPARs in EP4-dependent M2 polarization, peritoneal macrophages were pretreated with GSK3787 (PPARδ antagonist) (E), GW9662 (PPARγ antagonist) (F) or vehicle prior to the administration of IL-4/IL-13 and the EP4 agonist. Results are expressed as the fold induction of M2 genes compared with unantagonized, vehicle-treated cells. All values are mean ± SEM (n = 6 each). * p<0.05; ♯ p<0.01. LPS, lipopolysaccharide.