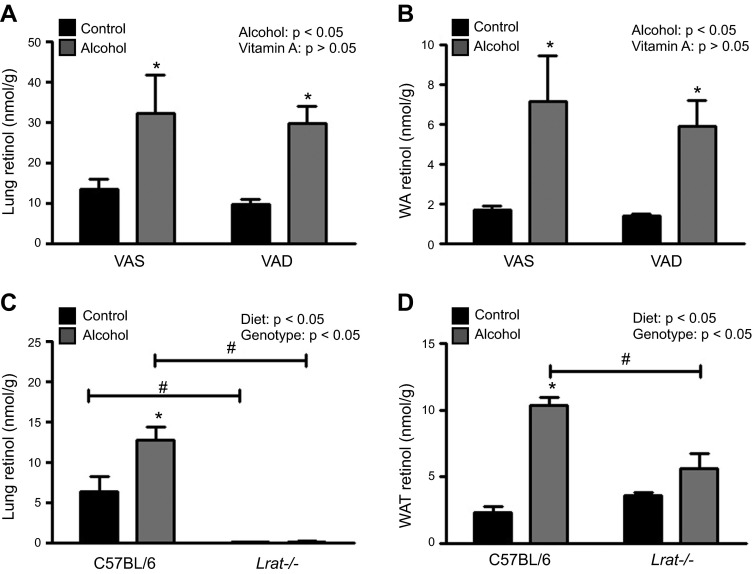
Figure 3.
The alcohol-induced increase in extrahepatic tissue retinol levels occur independent of dietary vitamin A intake and is blocked in Lrat−/− mice. Tissue retinol levels increased after the alcohol-adaptation period in (A) lung, and (B) WAT of alcohol-consuming mice fed a VAS (n = 4–6) or a VAD (n = 5–7) diet. Tissue retinol levels were increased in the (C) lung and (D) WAT of alcohol-consuming WT mice (n = 5), but this effect was blocked in Lrat−/− mice (n = 4). *P < 0.05 vs. animals of the same genotype; #P < 0.05 vs. animals consuming the same diet; 2-way ANOVA.