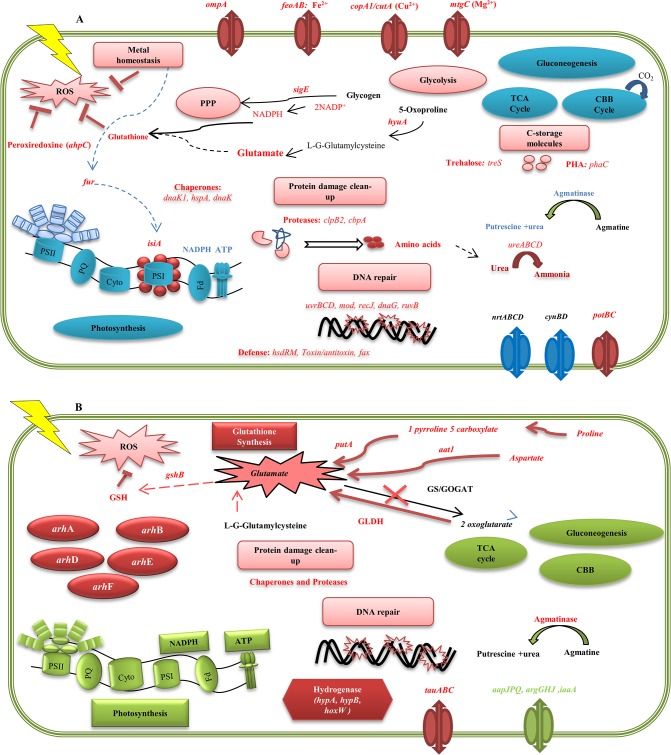
Fig 8. General overview of the main transcriptional response events of Arthrospira sp. PCC 8005 after exposure to 60Co gamma rays.
Schemes represent a global gene expression response (A) immediately after irradiation; (B) after 2H and 5H of recovery period. Blue colour, stand for down-regulated genes. Red colour stand for up-regulated genes, Green colour stand for restored expression of the initial silenced genes. (A) The largest changes in transcription occurred upon irradiation, as part of a kind of an “Emergency Response”. Cells displayed a reduced transcription for photosynthesis and energy production (PSII, PSI, ATP), and for carbon and nitrogen metabolism during irradiation. The CO2 fixation via the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle (CBB), glycogen biosynthesis (gluconeogenesis) and the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) were repressed. The transcription of the SigE regulator acting as nitrogen-dependent activator for catabolic genes towards glycogen degradation (glycolysis) was induced. Also a re-routing of the metabolic flux to glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) was seen. A synthesis of carbon storage molecules (PHA) and compatible solutes (trehalose) was seen. The expression of polyamine import (potBC), well known as a group of nitrogen-containing C-compounds which help in cell survival during stress, was recorded. The import of nitrate or cyanate as N-sources was repressed (nrtABCD, cynBD). In parallel also the metabolism of agmatine, a known competitive inhibitor of polyamine transport, was repressed. The cellular protection, detoxification, and repair were enhanced immediately after irradiation. In an effort to maintain the intracellular redox balance while provide sufficient metal-cofactors for enzymes, selective metal export (copA) and import (feoAB, cutA, corA, mtgC, cbiQ1, cbiQ2, znuA) was induced. There was upregulation of isiA gene encoding the CP43’ protein, which is an auxiliary antenna complex, to compensate for the loss of phycobilisomes. This protein may also serve as a chlorophyll storage molecule contributing to the reassembly of reaction centres during recovery. In addition, ROS detoxification was activated via the expression of the peroxiredoxine enzyme (ahpC) and the glutathione synthesis genes. The generation of glutathione starts at T0H via the formation of glutamate from proline by hyuA, from aspartate by aspartate aminotransferase (aat1), from 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate by (putA), and from 2-oxoglutarate via GLDH (see Fig 8B). Glutamate synthesis via the GS/GOGAT cycle was repressed. The final synthesis of glutathione from glutamate occurred via glutathione (GSH) synthase (gshB), which continued during recovery (see Fig 8B). Chaperones (dnaK1, dnaK2, hspA, cbpA) and proteases (clpB2) were also significantly induced during this stage, to remove damaged proteins. The free amino-acids released from protein degradation, likely lead to the production of urea, and the urease (ureABC) activity, transforming urea to ammonium, was induced. In parallel Arthrospira enhance some genes related to DNA repair system (uvrBCD for nucleotide excision and repair, ruvB resolving holiday junction, and recJ, dnaG and mod genes). The DNA-repair mechanism of Arthrospira included also enzymatic restriction modification (hsdr) and endonucleases. (B) During the later phase Arthrospira cells try to recover from the damage; which lead to a slowly restored expression of the genes related to photosynthesis and energy production, carbon fixation via the CBBn cycle and gluconeogenesis, TCA cycle. Expression of the hydrogenase genes (hypA1, hypB1and hoxW). Metal chaperone proteins HypA and HypB are required for the nickel insertion step of [NiFe]-hydrogenase maturation. In parallel slight reactivation of amino-acid transport (aapJPQ, argGHJ, iaaA) occurred. The genes for import of taurine (tauABC) known as organic sulphur and amino source were highly induced. The restoration of agmatinase, the key enzyme of agmatine hydrolysis was seen in recovery period. ROS detoxification was maintained efficiently via the expression for glutathione biosynthesis (GSH). Few genes related to protein damage clean up (proteases and chaperones) and DNA repair maintained their expression during recovery. The expression of gene cluster arhABCDEF, enriched during recovery, was seen.