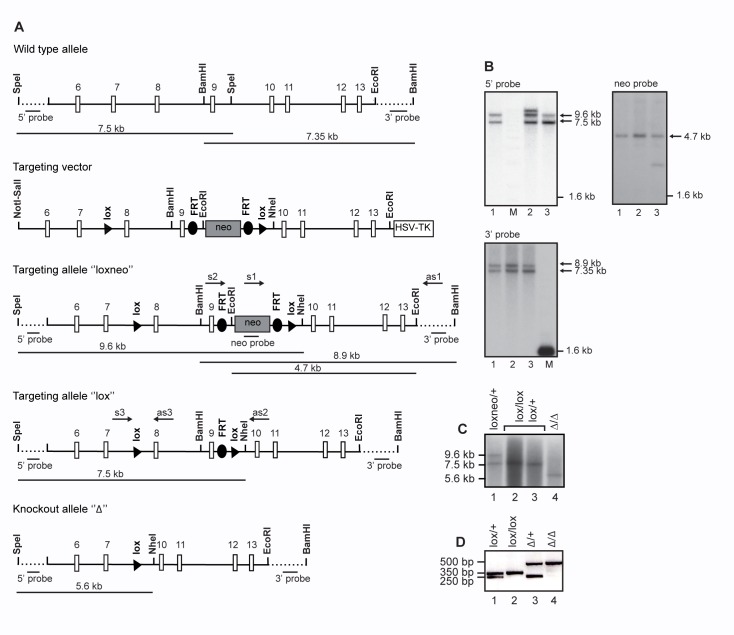
Fig 2. Inactivation of the CAP2/Tmprss4 gene locus.
(A) Scheme of the wild-type allele, the targeting vector, and the targeted CAP2/Tmprss4 loxneo allele following homologous recombination, and the CAP2/Tmprss4 lox and the CAP2/Tmprss4 Δ allele following breeding with Flp- and Cre-deleter mice, respectively. Relevant restriction enzymes for cloning and diagnosis of targeted ES cell clones are shown. Exons 8 and 9 and the neomycin cassette (flanked by frt sites) are flanked by loxP sites. 5’ and 3’ probes as well as PCR primers used for ES cell screening and mouse genotyping are indicated. (B) Southern blot analyses of targeted ES cell clones using the external 5’probe (upper left panel) following digestion with SpeI and NheI, the neo probe (upper right panel) following EcoRI digestion, and the external 3’probe following digestion with BamH1; note that clone #2 and #3 harbour additional recombination and integration events as evidenced by Southern blot analyses using the 5’ and neo probe, respectively. (C) Southern blot analysis of CAP2/Tmprss4 loxneo/+, CAP2/Tmprss4 lox/lox and/or CAP2/Tmprss4 lox/+ and CAP2/Tmprss Δ/Δ mice using the 5’ probe following SpeI/NheI digestion. (D) PCR-based genotyping of mice harbouring the wild type (+, 250bp, lane 1 and 3), lox alleles (lox, 350bp, lane 2) and knockout alleles (Δ, 500bp, lane 3 and 4).