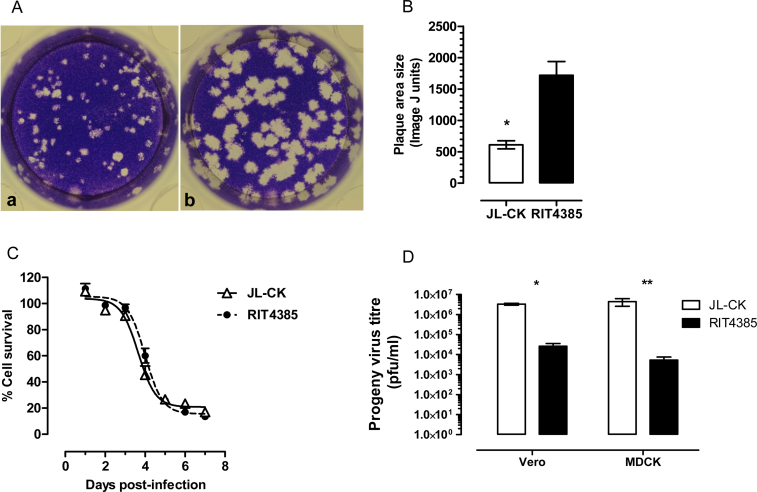
Fig. 1.
(A) Plaque morphology after infection of Vero cells. Panel a represents JL-CK and Panel b represents RIT4385. JL-CK produced a mixture of small and large plaques whereas RIT4385 formed a more homogeneous population of large plaques. (B) Measurement of plaque size of JL-CK and RIT4385 using ImageJ. The data shown is from JL-CK plaques (n = 25) and RIT4385 plaques (n = 33) (*p < 0.0001). (C) Growth kinetics of JL-CK and RIT4385 in Vero cells. JL-CK and RIT4385 were inoculated at MOI 0.0001 and lysed Vero cells at comparable rates. Viability of infected cells was expressed as the percentage of uninfected cells. Sigmoidal curves were fitted to the data points to calculate 50% cell lysis using GraphPad Prism 5 software (3.65 days for JL-CK and 3.99 days for RIT4385). The 95% confidence intervals overlapped (JL-CK, 3.89–4.42, RIT4385, 3.85–4.15 days). (D) JL-CK and RIT4385 progeny virus titres in Vero and MDCK cells. Infections were performed in two independent experiments each in triplicate, cells were infected at MOI 0.0001 and progeny viruses were titred in Vero cells after 7 days. JL-CK produced more progeny viruses on both Vero and MDCK cells (*p < 0.0001, **p = 0.0365), compared with RIT4385 on the same cell line (unpaired, two-tailed t-test).