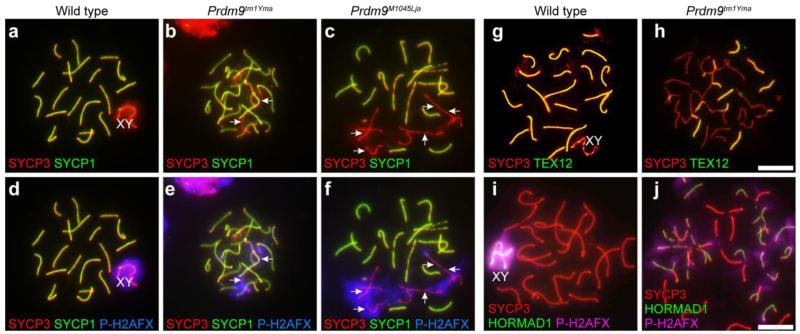
Fig. 8.
Aberrant synapsis in Prdm9-deficient spermatocytes. For these images chromatin spreads were prepared from juvenile testes and immunolabeled for components of the SC and DNA damage markers. Genotypes are designated for each vertical column. a-f: Spread chromatin preparations from wild type testes (a and d) and Prdm9-deficient testes (b-c and e-f) were immunolabeled with anti-SYCP1 (green), anti-SYCP3 (red), and anti-P-H2AFX (blue), revealing colocalization in mutant germ cells of asynapsis detected by absence of SYCP1 signal (arrows b-c) with P-H2AFX (arrows in e-f). a and d are the same cell, as are b and e, and c and f, respectively. g-j: Spread chromatin preparations from wild type testes (g and i) and Prdm9-deficient testes (h and j) were immunolabeled with anti-SYCP3 (red), anti-TEX12 (green in g and h), a component of the SC CE, or anti-P-H2AFX (pink in i and j) and anti-HORMAD1 (green in i and j), which marks regions of asynapsis. Patchy TEX12 label and persistence of HORMAD1 label on mutant chromosomes indicate numerous regions of asynapsis. Scale bars = 20 μm