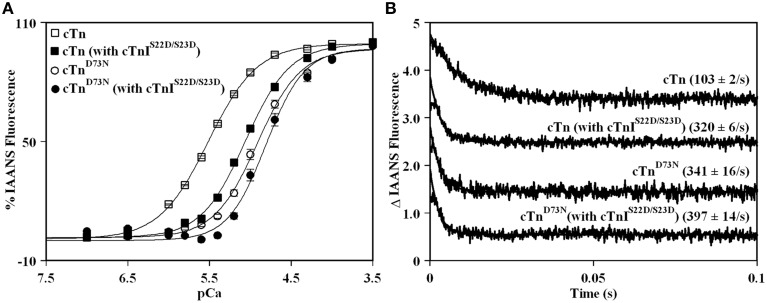
Figure 1.
Effect of the D73N mutation on the Ca2+ sensitivity and the rate of Ca2+ dissociation from reconstituted thin filaments in the absence and presence of cTnI pseudo-phosphorylation. (A) Increases in IAANS fluorescence, which occur as Ca2+ binds to the regulatory N-domain of the cTn complex, containing cTnI (□) or cTnIS22D/S23D (■), reconstituted into thin filaments; and to the regulatory N-domain of the cTnD73N complex, containing cTnI (◦) or cTnIS22D/S23D (•), reconstituted into thin filaments. Data represent the mean ± S.E. of at least three titrations fit with logistic sigmoid function. IAANS fluorescence was excited at 330 nm and monitored at 450 nm. (B) Time course of decreases in IAANS fluorescence as Ca2+ was removed by excess EGTA from the regulatory N-domain of the cTn complex, containing cTnI or cTnIS22D/S23D, reconstituted into thin filaments; and from the regulatory N-domain of the cTnD73N complex, containing cTnI or cTnIS22D/S23D, reconstituted into thin filaments. The data traces have been normalized and staggered for clarity. Each trace is an average of at least five traces fit with single exponential equation. The IAANS fluorescence was excited at 330 nm and monitored through a 510 nm bandpass filter.