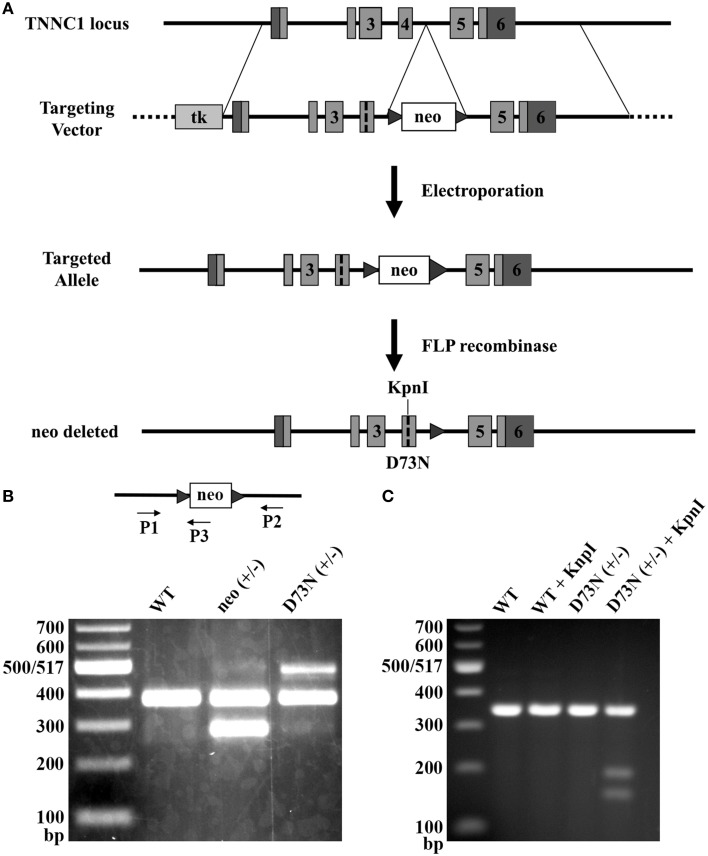
Figure 2.
Generation of knock-in mice. (A) The gene targeting strategy to introduce the D73N mutation in cTnC into mouse myocardium. Targeting vector harbored thymidine kinase (tk) gene, neo cassette flanked by FRT sites in intron 4, the D73N mutation and two silent substitutions in order to create a restriction site for the enzyme KpnI in exon 4. Targeting vector was introduced into ES cells by electroporation. Neo cassette was deleted by crossing neo (+/−) mice with mice expressing FLP recombinase to create the D73N (+/−) mice. (B) PCR mediated genotyping of WT, neo (+/−), and the D73N (+/−) mice. Product lengths are 384, 287, and 517 base pairs for WT, neo, and D73N alleles, respectively. (C) Undigested and digested RT-PCR products for WT and the D73N (+/−) mice. KpnI restriction site was present in the D73N (+/−) mice but not in WT mice. Total RNA was isolated from the left ventricle of four hearts per genotype, with each KpnI digestion conducted in triplicate.