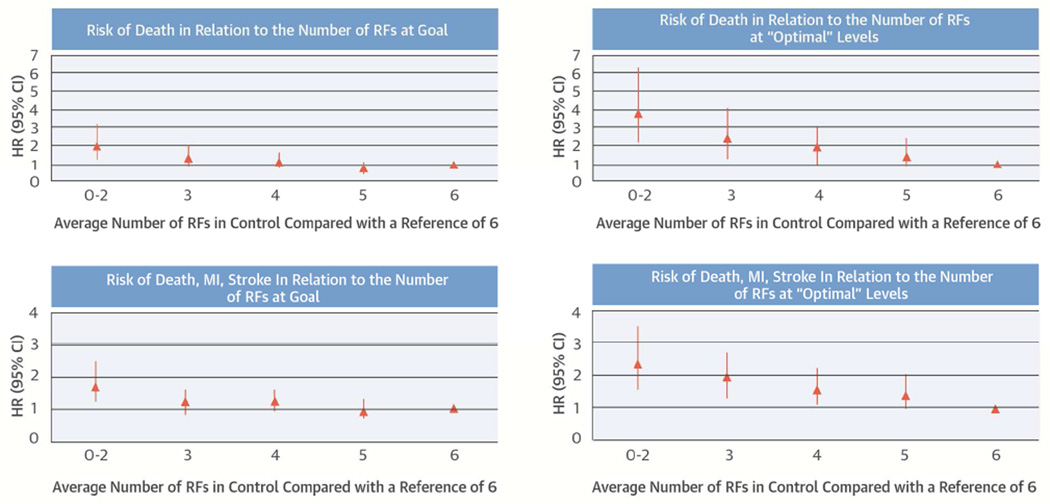
Central Illustration. Cardiac RF Control Improves Survival: Number of RFs in Control and Outcomes.
The number of RFs in control is plotted against mortality (A and B) and against CVD events (C and D). In panels A and C, RFs in control are defined on the basis of the BARI 2D protocol (main analysis). A J-shape is evident: individuals with 6 RFs in control have a numerically higher risk of events than those with 5 RFs in control. In panels B and D, “optimal ranges” are defined for systolic and diastolic BP and HbA1c. A J-shape is no longer evident and the risk gradient comparing 6 versus 0 to 2 RFs in control is steeper. BP = blood pressure; CVD = cardiovascular disease; HbA1c = glycosylated hemoglobin; HR = hazard ratio; MI = myocardial infarction; RF = risk factor.