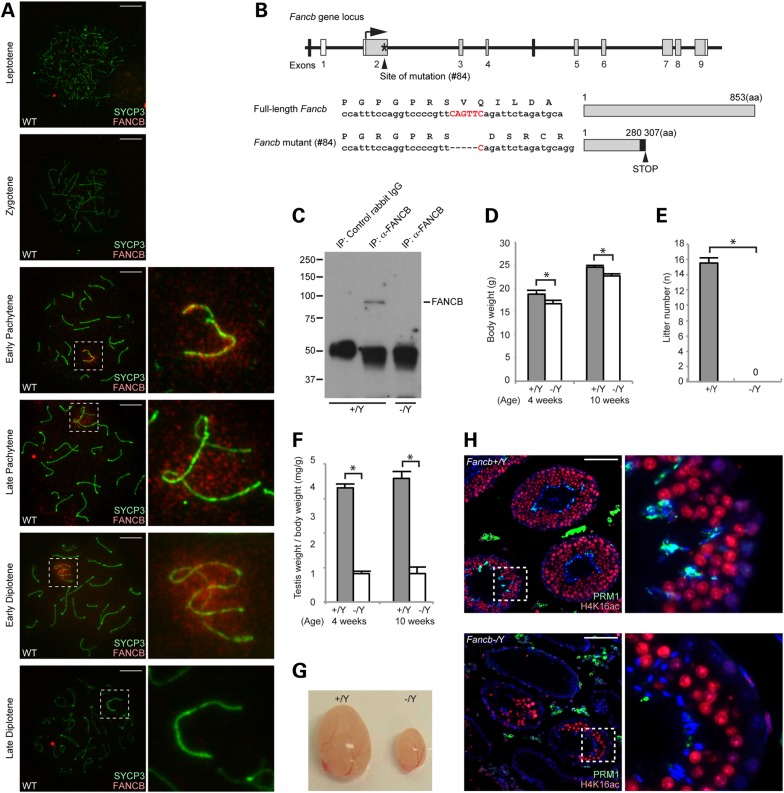
Figure 1.
FANCB localization on meiotic sex chromosomes and generation of Fancb mutant mice. (A) Immunostaining of meiotic chromosome spreads using an anti-mouse FANCB antibody. SYCP3 is a marker for meiotic chromosome axes. Dotted squares represent the areas surrounding sex chromosomes, and the areas are magnified in the right panels. Scale bars: 10 µm. (B) Structure of Fancb gene and FANCB protein. The site of ZFN-induced mutation of line #84 mutant mice is shown. Asterisk indicates targeting site. White boxes represent non-coding regions, and gray boxes represent coding regions. The mutation leads to a frame change (shown with a black box) and a premature stop codon. (C) Immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis showing the absence of full-length FANCB protein in Fancb mutant testes. (D) Body weights compared for wild-type and Fancb mutant mice at 4 and 10 weeks after birth. Mean and SEM for independent mice are shown. Numbers of mice analyzed at 4 and 10 weeks, respectively: seven and six wild-type, and seven and six Fancb mutant mice. *P < 0.05. Unpaired t-test. (E) Fertility test: mean numbers of litters and SEM for independent mice are shown. Numbers of mice tested: seven wild-type and seven Fancb mutant mice. P < 0.05. Unpaired t-test. (F) Testis weights/body weight (mg/g) of wild-type and Fancb mutant mice at 4 and 10 weeks. Mean and SEM for independent mice are shown. Numbers of mice analyzed at 4 and 10 weeks, respectively: seven and six wild-type, and seven and six Fancb mutant mice. *P < 0.05. Unpaired t-test. (G) Representative photo of the testes of wild-type and Fancb mutant mice. (H) Immunostaining of testicular sections for H4K16 acetylation and protamine 1 (PRM1) from 10-week-old wild-type and Fancb mutant mice. Scale bars: 100 µm. The areas shown with white dotted squares are magnified in the right panels.