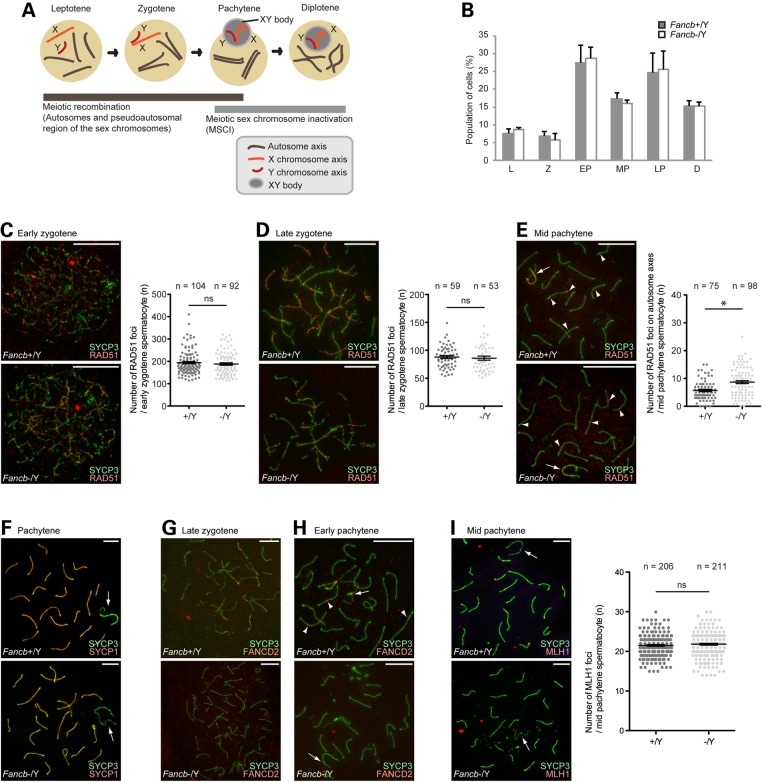
Figure 4.
Roles of FANCB in meiotic recombination. (A) Schematic of meiotic prophase and the involvement of two DDR events. (B) The percentage of each stage of meiotic prophase as judged by SYCP3 immunostaining. Total numbers of cells analyzed: 263 from wild-type, and 230 from Fancb mutant mice. Mean and SEM for independent mice are shown. Three independent mice were analyzed for each dataset. (C–I) Immunostaining of chromosome spreads. Scale bars: 10 µm. (C–E) RAD51 foci in zygotene and pachytene spermatocytes. In the right panels: scoring of the number of RAD51 foci per cell at the indicated stages. Distribution of data is shown as dots; mean ± SEM for independent mice is shown as bars. Total numbers of analyzed nuclei are indicated in the panels. For each panel, four independent mice were analyzed for both wild-type and Fancb mutant mice. (F) SYCP1 localization in pachytene spermatocytes. (G and H) FANCD2 foci in zygotene and pachytene spermatocytes. (I) MLH1 foci in pachytene spermatocytes. In the right panel: scoring of the number of MLH1 foci per cell at the mid pachytene stage. Distribution of data is shown as dots; mean ± SEM for independent mice is shown as bars. Total numbers of analyzed nuclei are indicated in the panel. Five independent mice were analyzed for both wild-type and Fancb mutant mice. Arrows: sex chromosomes; arrowheads: RAD51 foci in panel (E) and FANCD2 foci in panel (H). *P < 0.05. ns: not significant. Unpaired t-test.