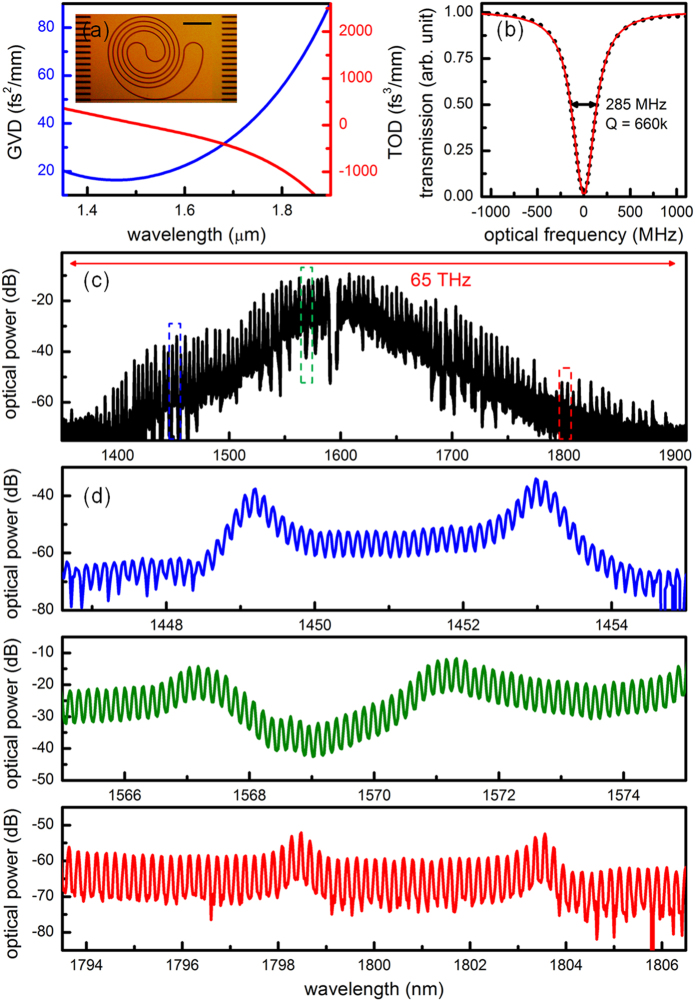
Figure 1. A phase-locked 18 GHz Kerr frequency comb spanning over 65 THz.
(a), Simulated group velocity dispersion (GVD) and third order dispersion (TOD) of the ring resonator, featuring small TOD which is beneficial for broad comb generation. Inset: An optical micrograph of the spiral resonator, with a total cavity length of 8.04 mm and a mode area of 1.3 μm2. Adiabatic mode converters (the dark bars on the side of the chip) are implemented to improve the coupling efficiency from the free space to the bus waveguide (the bottom straight line across the chip). Scale bar: 250 μm. (b), Example critically-coupled resonant pump mode at 1595.692 nm, with a 285 MHz loaded cavity linewidth. Black dots are the measured data points and the red curve is the fitted Lorentzian lineshape. (c), Example generated Kerr frequency comb, with a broad spectrum spanning nearly half an octave at 65 THz and covering multiple telecommunication bands (E, S, C, L and U bands). (d), Zoom-in views of the comb spectra from 1446.5 nm to 1455 nm (blue), 1565 nm to 1575 nm (green), and 1793.5 nm to 1806.5 nm (red). Even in the wings of the spectrum, native-FSR-spacing comb lines are clearly observed.