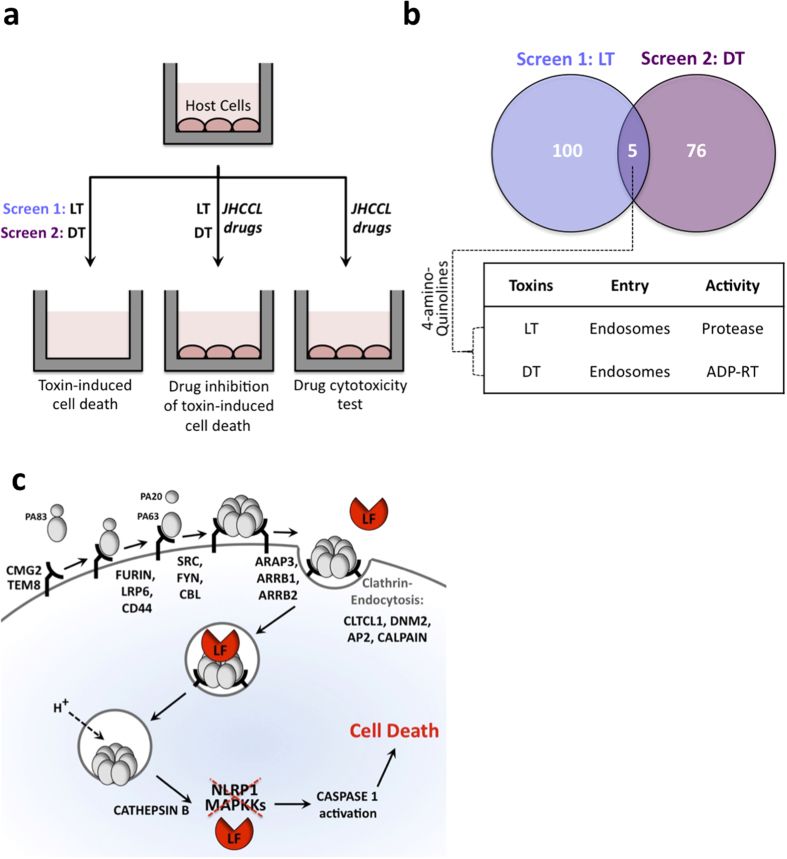
Figure 1. The use of Johns Hopkins Clinical Compound Library (JHCCL) to screen for inhibitors of bacterial toxins.
(a) Schematic diagram of cellular screens to identify drugs that reduce cellular lethality induced by anthrax lethal toxin, LF and PA (LT) and diphtheria toxin (DT). (b) The distribution of inhibitors obtained in those screens, with a table showing the routes taken by toxins to enter into cellular cytoplasm (Endocytosis), as well as the enzymatic activities of toxins (Protease or ADP-rybosyltransferase (ADP-RT)). (c) Schematic depiction of the host pathway that mediates the delivery of anthrax toxin into cytoplasm. Lethal factor (LF) and edema factor (EF) interact with a third B. anthracis-generated protein, protective antigen (PA). Three host cell proteins CMG2, TEM8, and ITGB1 can serve as receptors for the bipartite PA/LF and PA/EF toxins. Fifteen additional host proteins are known to assist PA binding and/or internalization.