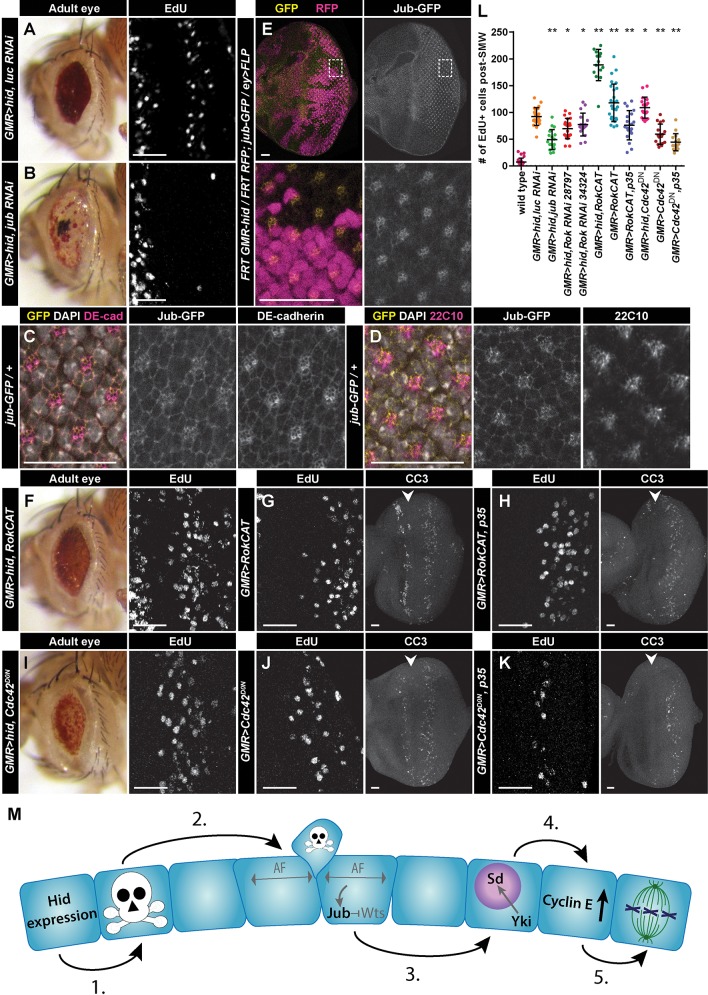
Fig. 6.
Jub and cellular tension regulate compensatory proliferation. (A,B,F,I) Adult eyes (left panels) and high magnification of post-furrow EdU staining (right panels) of the indicated genotypes. (C,D) Jub-GFP (yellow) colocalizes with DE-cadherin (magenta; C) and Futsch/22C10, a marker of neuronal membranes (magenta; D), at the apical surface of post-furrow eye discs. (E) Clones of GMR-hid (no marker) and wild-type (RFP+, magenta) cells expressing Jub-GFP (yellow). Boxes in top panels indicate area of magnification shown in bottom panels. (G,H,J,K) High magnification of post-furrow EdU staining (left panels) and CC3 staining (right panels) of the indicated genotypes. Arrowheads mark the MF. GMR>RokCAT (G) and GMR>Cdc42DN (J) induce CC3-positive apoptotic cells posterior to the MF. Interestingly, apoptotic cells are also observed anterior to the furrow in these discs. The mechanism triggering this apoptosis is unknown, but its absence in GMR>RokCAT, p35 (H) or GMR>Cdc42DN, p35 (K) discs suggests the anterior induction of apoptosis in GMR>RokCAT and GMR>Cdc42DN discs is dependent on apoptosis posterior to the furrow. CC3 staining persists posterior to the furrow after p35 expression (H,K) because undead cells express non-cleaved-caspase epitopes of the anti-CC3 antibodies (Fan and Bergmann, 2010). (L) Quantification of CP in the indicated genotypes. GMR>hid, Gal4 genotypes were compared with GMR>hid, luc RNAi, whereas GMR>Gal4 genotypes were compared with wild type (w1118). Each circle represents the number of cells counted for a single disc, and bars represent mean and one standard deviation. For each genotype, n≥14 discs. *P≤0.02, **P≤1×10−7. (M) Model for induction of CP in a quiescent epithelium. Text in gray indicates proposed possibilities that have not formally been observed in this study. (1) Hid expression/tissue damage induces apoptosis in a subset of cells. (2) Basal extrusion of apoptotic cells induces apoptotic force (AF), which activates Jub, leading to Wts inhibition. (3) Wts inhibition results in Yki translocating to the nucleus and acting as a transcriptional co-activator for Sd. (4) Sd/Yki induce high levels of Cyclin E, which induces cell cycle re-entry (5). Anterior is oriented to the left. Scale bars: 20 μm.