Table 1.
Examining organic hydrogen acceptors for oxidative esterification.[a]

| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|

|

|
|
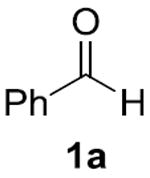
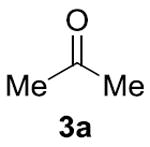
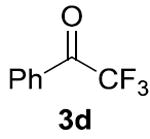
| 47% (5.9:1) | 35% (4.4:1)[c] | 12% (2.4:1) | 78% (8.7:1)[e] | 95% (48:1)[f] |
| 98% (5.5:1)[b] | 10% (>99:1)[c, d] | |||
Conditions: 0.1 mmol 1a, 0.1 mmol 2a, 0.2 M. Yields were determined by GC analysis using dodecane as an internal standard. IPr = 1,3-Bis(2,6- diisopropylphenyl)imidazole-2-ylidene. Yield of product 4a is shown, and the ratio of 4a:5a is shown in parentheses.
Using 2.5 equivalents of 1a.
Reaction performed at 80 °C.
Using 100 equivalents of 3a.
Using 3 equivalents of 3c.
Reaction performed at 30 °C.
