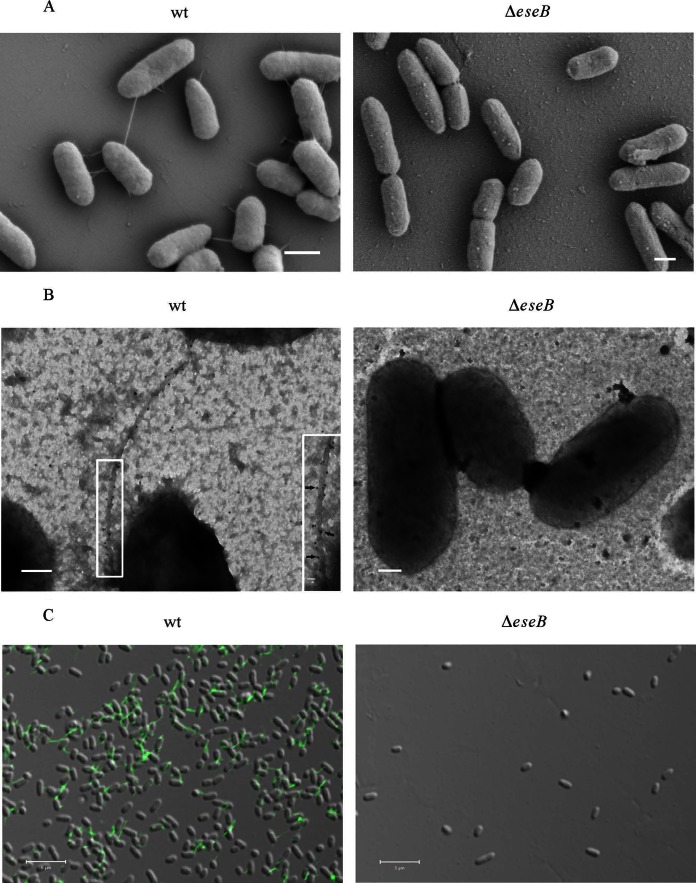
FIG 2.
EseB forms filamentous appendages on the surface of E. tarda cells. (A) SEM of E. tarda wild-type strain PPD130/91 and the ΔeseB strain. Bars, 600 nm. (B) Immuno-TEM images of the E. tarda wild-type and ΔeseB strains. Bacteria were labeled with anti-EseB antibody and protein A-coated colloidal gold particles conjugated to donkey anti-mouse secondary antibody (10 nm in diameter). Gold particles were distributed along filamentous appendages on E. tarda wild-type (black arrows) but not on ΔeseB cells. The inset shows enlarged views of the boxed areas. Bars, 200 nm; bar for the inset, 20 nm. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of wild-type and ΔeseB cells with antibody against EseB. The fixed bacteria were incubated with anti-EseB antibody, followed by incubation with Alexa 488 donkey anti-mouse secondary antibody. Green filamentous signals were detected in wild-type bacteria but not in ΔeseB strain bacteria. Bars, 5 μm.