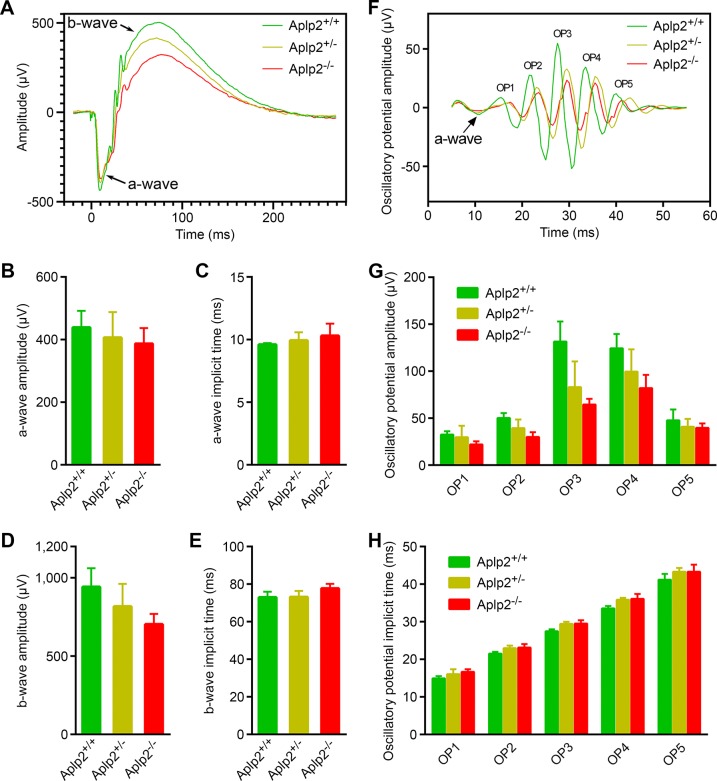
Fig 5. Analysis of scotopic electroretinograms in the Aplp2 knockout mice.
(A-E) Effect of targeted deletion of Aplp2 on the a-wave and b-wave. Lack of Aplp2 causes a dose-dependent decrease in the b-wave amplitude (F(2, 18) = 6.9, p = 6.0 × 10−3). The b-wave implicit time was increased in the Aplp2 knockouts compared to both heterozygous and wild-type littermates (F(2, 18) = 6.1, p = 9.6 × 10−3). Lack of Aplp2 did not have significant impact on either a-wave amplitude or a-wave implicit time (F(2, 18) = 0.8, p = 0.47, amplitude; F(2, 18) = 2.6, p = 0.1, implicit time). (F-H) Effect of targeted deletion of Aplp2 on oscillatory potentials. The amplitude of the oscillatory potentials (OP) exhibited a dose-dependent decrease in the Aplp2 knockout mice, while the OP implicit time was increased in both heterozygous and knockout animals compared to the wild-type littermates. OP1 amplitude: F(2, 18) = 3.6, p = 5.0 × 10−2; OP2 amplitude: F(2, 18) = 15.6, p = 1.0 × 10−4; OP3 amplitude: F(2, 18) = 20.5, p < 1.0 × 10−4; OP4 amplitude: F(2, 18) = 9.7, p = 1.0 × 10−3; OP5 amplitude: F(2, 18) = 1.9, p = 0.2; OP1 implicit time: F(2, 18) = 7.2, p = 5.0 × 10−3; OP2 implicit time: F(2, 18) = 10.9, p = 8.0 × 10−4; OP3 implicit time: F(2, 18) = 20.9, p < 1.0 × 10−4; OP4 implicit time: F(2, 18) = 17.7, p < 1.0 × 10−4; OP5 implicit time: F(2, 18) = 4.5, p = 3.0 × 10−2. Error bars, s.d.; n = 7.