Fig. 1.
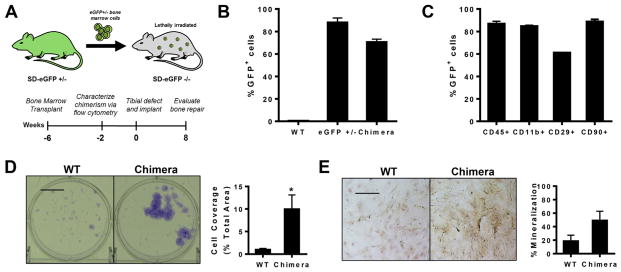
Rat bone marrow chimeras as a model for studying bone regeneration. (A) Sprague–Dawley rat bone marrow chimeras were generated by transplanting eGFP+ bone marrow into lethally irradiated eGFP−/− rats. Tibial defects were created 6 weeks post-transplantation. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of eGFP expression in blood 4 weeks post-bone marrow transplantation demonstrated stable reconstitution of the hematopoietic system with GFP+ cells, n = 3–4. (C) GFP+ cells display multi-lineage differentiation as assessed by flow cytometry analysis of blood taken 4 weeks post-transplantation, n = 3. (D) Bone marrow from chimeras after 7 days of culture as observed with crystal violet staining (left) and quantification of colony coverage (right), n = 6. (E) Bone marrow from eGFP chimeras after 7 days of culture in osteogenic media as observed with Alizarin red staining (left) and quantification of mineralized area (right), n = 3. Scale bar, 100 μm; *p < 0.05. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
