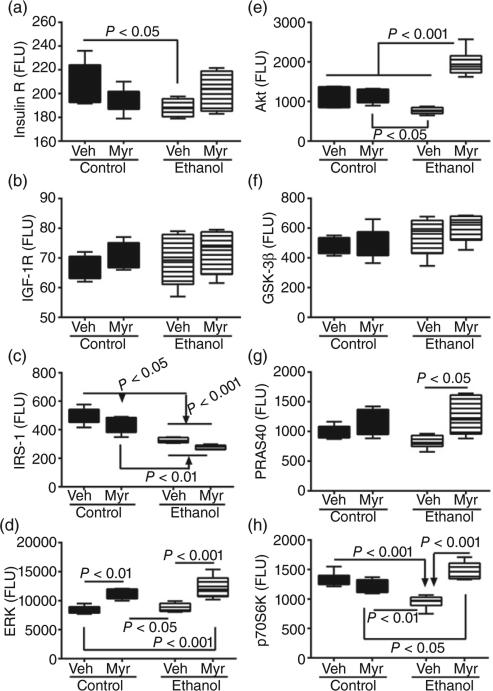
Figure 3.
Chronic ethanol feeding and myriocin treatment effects on hepatic insulin, insulin growth factor (IGF) and insulin receptor substrate (IRS) signaling mechanisms. Liver tissue from control and chronic ethanol-fed rats that were treated with vehicle (Veh) or myriocin (Myr) was used to measure (a) insulin receptor, (b) IGF-1 receptor, (c) IRS-1, (d) extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2, (e) Akt, (f) glycogen synthase kinase 3β, (g) proline-rich Akt substrate 40 kDa, and (h) p70S6 kinase by multiplex or single-plex ELISA. Results were normalized to protein content in reactions; n = 8 or 10 samples per group. Box plots depict medians (horizontal bars), 95% confidence intervals (upper and lower limits of boxes), and ranges (stems). Intergroup comparisons were made by repeated-measures one-way anova with post hoc Tukey tests. FLU, fluorescent light units.