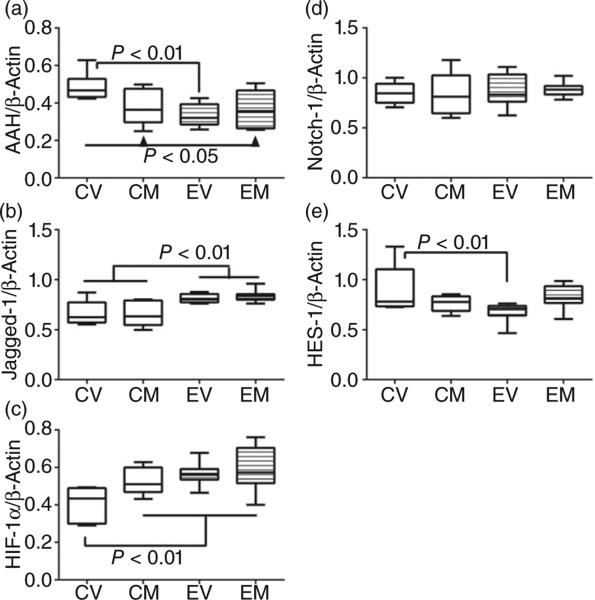
Figure 5.
Effects of chronic ethanol exposure and myriocin treatment on aspartyl-asparaginyl-β-hydroxylase (AAH) and Notch signaling-related mRNAs in liver. Livers from control and chronic ethanol-fed rats that were treated with vehicle or myriocin were used to measure (a) AAH, (b) Jagged-1, (c) hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, (d) Notch-1, and (e) Hairy–Enhancer of Split-1 mRNA levels in probe hydrolysis-based quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assays. Results were normalized to β-actin, which was measured simultaneously. Intergroup comparisons were made using the calculated mRNA/β-actin ratios. CV, control + vehicle; CM, control + myriocin; EV, ethanol + vehicle; EM, ethanol + myriocin; n = 8 or 10 samples per group. Box plots depict medians (horizontal bars), 95% confidence intervals (upper and lower limits of boxes), and ranges (stems). Intergroup comparisons were made by repeated-measures one-way anova with post hoc Tukey tests of significance.